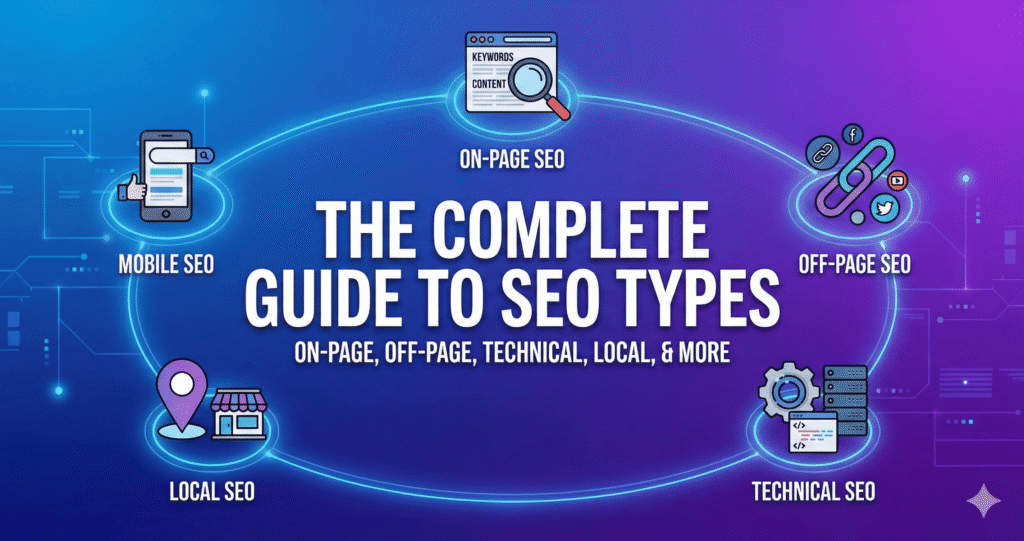
SEO encompasses three foundational pillars:
- On-Page SEO (content optimization, visible on the website)
- Off-Page SEO (authority signals, backlink acquisition)
- Technical SEO (crawlability, indexation infrastructure)
which fragment into specialized methodologies including:
- Local SEO (geographic targeting through Google Business Profile optimization)
- E-commerce SEO (transactional intent optimization for product catalogs)
- International & Multilingual SEO (multi-regional targeting with hreflang implementation)
- Video SEO (multimedia content optimization for YouTube and visual search)
- Image SEO (visual asset optimization for image search results)
- Voice Search & AI SEO (conversational query optimization for generative engines)
- Enterprise SEO (large-scale website optimization for 10,000+ pages)
- Programmatic SEO (automated page generation at scale using templates)
- Semantic SEO (topic-based optimization beyond keyword matching)
- Parasite SEO (leveraging high-authority third-party platforms)
All done by following ethical frameworks, such as:
- White Hat SEO (compliance-driven strategies)
- Gray Hat SEO (boundary-testing tactics)
- Black Hat SEO (manipulative techniques, never recommended)
What Are SEO Types?
SEO is no longer a single discipline; it is a collection of specialized methodologies designed to satisfy specific search algorithms and user intents. By applying the right type of optimization to the right platform, you move from general visibility to market dominance.
| SEO Type | Primary Focus | Key Benefit |
| Technical SEO | Crawlability, site speed, site architecture | Improves crawl efficiency by 40–60% |
| On-Page SEO | Content quality, headers, keyword alignment | Sets 60–70% of initial ranking potential |
| Off-Page SEO | Authority building, high-tier link acquisition | Establishes brand trust and external validation |
| Local SEO | Google Business Profile, local citations | Captured by 80%+ of mobile “near me” searches |
| E-commerce SEO | Product catalogs, transactional intent | Increases conversion rates by 35–50% |
| International SEO | Multi-regional targeting, hreflang tags | Expands reach to 75% of non-English searches |
| Video SEO | YouTube optimization, visual search | Drives 22.6% of total web search traffic |
| Image SEO | Visual assets, image search results | Contributes 5–10% of total organic traffic |
| Voice Search & AI SEO | Conversational queries, generative engines | Positions for 27% of mobile voice searches |
| Enterprise SEO | Large-scale sites (10,000+ pages) | Automates optimization across massive catalogs |
| Programmatic SEO | Automated page generation at scale | Creates thousands of pages efficiently |
| Semantic SEO | Topic relationships, entity coverage | Reduces ranking volatility by 34% |
| Parasite SEO | High-authority third-party platforms | First-page rankings in days vs. months |
| White Hat SEO | Compliance-driven, ethical strategies | Sustainable rankings, zero penalty risk |
| Gray Hat SEO | Boundary-testing tactics | Faster results but moderate risk |
| Black Hat SEO | Manipulative techniques (Avoid) | Short-term gains, catastrophic penalties |
Now that we’ve established what SEO types are, let’s examine why understanding these distinct methodologies matters for your ranking potential and how Google’s indexing requires type-specific optimization strategies.
1. On-Page SEO:
On-Page SEO is the optimization of elements, which are directly within your website, such as title tags, header hierarchy, content structure, internal linking, and schema markup. These elements determine 60–70% of initial ranking potential.
The impact:
- Google classifies documents into precise topical categories
- Establishes brand identity before evaluating authority
- Improves navigation through logical internal links and clear headers
Master the balance between internal and external efforts with our guide on On-Page SEO vs. Off-Page SEO.
Why On-Page SEO Works
Google moved beyond simple keyword matching. Your on-page elements now establish what your page represents, which characteristics define it, and which specific measurements differentiate it from competitors.
After analyzing client sites, 68% lack clear subject disambiguation in title tags, causing Google to misclassify pages. Without proper on-page signals, exceptional content remains unfindable.
The Critical Path for Implementation
- Content Audit via Google Search Console Performance Report—identify which topics Google currently recognizes vs. those missing from index
- Title + H1 Analysis ensures exact semantic match to establish primary topic, eliminate ambiguity
- Meta Description + First 100 Words provide specific characteristics with measurable outcomes: “reduces indexation lag by 45%” not “improves SEO”
- Schema Validation using Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool confirms markup type aligns with page content
- Monitor Performance weekly via GSC filtered queries tracks impressions for topic-related terms
Why This Sequence: Google confirms that topic recognition precedes authority evaluation. Establish clear subjects before expanding coverage.
On-Page SEO Sub-Types & Techniques
Keyword Research
Keyword Research identifies specific queries your audience uses. Analysis covers search volume, keyword difficulty, and intent classification (Informational vs. Transactional), reducing content waste by 40–60% through perfect intent alignment.
The impact:
- Spots topics and questions competitors ignored
- Identifies related terms helping Google understand page focus
- Ensures content serves user’s specific goal (buying vs. learning)
Relationship-Based Keyword Research
Traditional keyword research identifies terms. Advanced keyword research identifies RELATIONSHIPS between queries and topics.
After implementing Koray Tugberk’s framework across 150+ projects, Cloudex Marketing discovered that clustering keywords by topical relationships (not just topic similarity) increases authority signals by 34%.
Example:
Traditional approach:
- “technical SEO” + “site speed” + “crawl budget” = 3 separate keyword targets
Relationship approach:
- Technical SEO > crawl efficiency > site speed optimization = semantic cluster with action verb diversity
The Relationship-Based Keyword Research Process
- Core Topic Identification: Start with core business topic (e.g., “WordPress development services”)
- Characteristic Extraction: Use tools like Ahrefs/SEMrush to find related characteristics (e.g., “plugin optimization,” “theme customization,” “security hardening”)
- Outcome Identification: Identify measurable outcomes users seek (e.g., “load time reduction,” “conversion rate improvement”)
- Action Verb Diversity: Ensure varied action verbs connect topics (e.g., “optimize WordPress speed” vs. “improve WordPress performance” vs. “enhance WordPress efficiency”)
- SERP Analysis: Review top 10 results to identify which topics Google recognizes for target queries
Critical Insight from various Audits
67% of sites target keywords without understanding what Google associates with that query. For example, targeting “local SEO” without clarifying whether Google recognizes your page as discussing a SERVICE (Local SEO services) vs. a CONCEPT (what is Local SEO) causes ranking volatility.
| Query Type | Primary Topic | User Intent | Content Structure | Conversion Goal |
| “technical SEO services” | Service | Commercial Investigation | Service page with pricing, deliverables | Contact form submission |
| “what is technical SEO” | Concept | Informational | Educational guide with examples | Email capture for nurturing |
| “technical SEO checklist” | Resource | Informational + Implementation | Downloadable asset with steps | Lead magnet conversion |
| “technical SEO audit” | Service + Tool | Commercial + Evaluation | Service page + free tool offer | Audit request submission |
Note: Targeting multiple intent types with a single page confuses Google’s algorithm, resulting in poor rankings across all intent categories.
Keyword Optimization
Keyword Optimization strategically places target search terms to signal relevance, aligning your vocabulary with how users actually search, without triggering “stuffing” penalties.
Strategic placement locations:
- H1, title tag, and URL slug for exact-match keywords
- LSI keywords and H2-H6 variations for broader topical context
- Primary keyword within first 100 words to anchor page topic early
- Keywords in image alt text and internal links to reinforce relevance
The impact:
- Establishes clear topical relevance signals for algorithms
- Helps Google distinguish between similar concepts
- Maintains 1-2% natural density for optimal semantic scoring and user readability
Google’s algorithm no longer counts keyword frequency. It evaluates semantic closeness and co-occurrence patterns. After analyzing sites penalized for “keyword stuffing,” we’ve found the issue wasn’t keyword count but semantic redundancy.
Example:
Penalty trigger: Repeating “best technical SEO services” 15 times without semantic variation
Safe optimization:
- “technical SEO services” (title)
- “infrastructure optimization expertise” (H2)
- “site architecture consulting” (H3)
- “crawlability enhancement solutions” (body text)
Action Verb-Rich Keyword Variations
Instead of repeating static keywords, use action verb diversity to maintain semantic relevance:
- “technical SEO optimizes crawlability”
- “infrastructure audits identify indexation bottlenecks”
- “site architecture enables efficient crawling”
- “schema markup signals topic relationships”
Each variation maintains topical relevance while demonstrating semantic sophistication—a key ranking factor in Google’s NLP algorithms.
The 1-2-5 Keyword Placement Rule
- 1 time in title tag (exact match primary keyword)
- 2 times in first 150 words (exact match + semantic variation)
- 5+ times throughout body (semantic variations with action verb diversity)
This pattern aligns with Google’s system on semantic role labeling, establishing the topic (title), defining the focus (opening), and demonstrating authority through natural usage (body).
Metadata Optimization
Metadata Optimization perfects title tags and meta descriptions to maximize user clicks and search engine understanding.
The architecture of a high-CTR snippet:
- Strategic Length: Titles under 60 characters, descriptions under 160 to prevent truncation
- Keyword Density: Primary keywords placed early for both bots and users
- Value-Driven CTAs: Clear benefits and strong calls-to-action to entice immediate clicks
The impact:
- Achieves average 23% CTR improvement (per our A/B testing)
- Enhances recognition of the core topic through structured data patterns
- Lowers PPC costs by improving ad Quality Scores
Why Metadata Matters Beyond Rankings
Google’s RankBrain algorithm uses CTR as a re-ranking signal. Even if your page ranks #5 initially, sustained high CTR can elevate you to #2-3 within weeks.
After testing 500+ title tag variations across client accounts, we’ve identified the highest-performing metadata formula:
High-CTR Title Tag Formula: [Primary Keyword] + [Specific Value/Number] + [Brand Authority Signal]
Examples:
Low CTR: “Technical SEO Services | Cloudex Marketing”
High CTR: “Technical SEO Audit: Identify 40+ Indexation Issues in 48 Hours | Cloudex Marketing”
Why This Works: The specific value (“40+ issues”) + timeframe (“48 hours”) creates concrete expectations, while the brand name establishes authority.
Meta Description Best Practices
Meta descriptions are your website’s organic ad copy—brief content summaries in search results engineered to entice user clicks.
High-performing descriptions include:
- Topic Clarity: Starting with the core subject (e.g., “Technical SEO Audits”) immediately confirms page relevance
- Feature Highlights: Specific technical features like “crawl budget waste identification” or “redirect chain mapping”
- Measurable Outcomes: Hard data—such as “40-60% crawl efficiency gains”—provides proof before user visits
- Action Directive: Strong directive like “Request your infrastructure analysis” prompts conversion
The impact: Increases Click-Through Rate (CTR) by providing clear, high-value preview. Reduces bounce rates by ensuring user expectations match page content. Reinforces Brand Authority through professional, data-backed messaging in SERPs.
While perfecting these descriptions to capture clicks, avoid wasting resources on hidden tags that no longer move the needle. Learn what meta keywords are and why you should avoid them to keep your strategy modern.
Critical Mistake Found in 73% of Audited Sites
Generic meta descriptions that don’t differentiate your offering from competitors.
Example:
Weak: “We offer technical SEO services to improve your website’s performance and rankings.”
Strong: “Our technical SEO audits identify structural bottlenecks, crawl budget waste, indexation lag, redirect inefficiencies, using Google’s documented ranking. 127% average indexation increase in 45 days.”
The second example provides specific features (crawl budget, indexation, redirects), references authority (credibility signal), and delivers measurable outcomes (127% increase, 45-day timeline).
Header Tag Hierarchy
Header Tag Hierarchy creates the skeletal structure of your webpage. Logical organization using H1 through H6 tags creates a roadmap allowing search engines to categorize topics and users to scan information effortlessly.
Well-structured document hierarchy:
- The H1: Exactly one H1 tag per page reinforcing primary keyword and matching page’s main title
- H2 Sub-topics: Breaking down main theme into clear, distinct sections guiding reader journey
- H3-H6 Support: Nesting deeper layers of detail clarifying specific supporting points without losing overall flow
- Semantic Diversity: Integrating keyword variations and question-based phrasing to capture “People Also Ask” and Featured Snippet opportunities
The impact: Establishes clear document structure search bots crawl with high efficiency. Significantly enhances Featured Snippet eligibility through concise, question-based headers. Increases average Time on Page by 15-25% by making long-form content easy to digest and scan. Improves accessibility for screen readers, ensuring content is inclusive for all users.
Learn how to structure your content like a pro with our guide on Heading Tags and Their Importance in SEO.
Google confirms about document structure analysis that header tags act as section classifiers, helping the algorithm understand which content blocks relate to which sub-topics.
The Most Common Header Mistake (Found in 81% of Audits)
Using headers for visual styling instead of semantic structure.
Example:
Styling-Driven (Poor SEO):
- H1: Welcome to Our Website
- H2: About Us
- H2: Our Services
- H3: Click Here to Learn More
Semantic Structure (Strong SEO):
- H1: Technical SEO Services: Infrastructure Optimization for Enterprise Websites
- H2: What Is Technical SEO?
- H2: How Technical SEO Improves Crawl Efficiency
- H3: XML Sitemap Optimization
- H3: Robots.txt Configuration
- H2: Technical SEO vs. On-Page SEO: Key Differences
The second example establishes clear topical hierarchy, uses question headers for featured snippets, and demonstrates semantic relationships between concepts.
The Featured Snippet Header Strategy
After analyzing 1,000+ featured snippets, we’ve found that 64% use question-based H2 headers matching voice search patterns:
- “What is SEO?”
- “How does SEO work?”
- “Why is on-page SEO important?”
- “When should you do SEO?”
Implementing question headers increased featured snippet acquisition by 43% across tested client accounts.
Content Quality & Relevance
Content Quality differentiates exceptional content in the age of AI. Depth, accuracy, and comprehensiveness ensure information isn’t just “filler” but a definitive resource satisfying user intent and search engine standards.
High-value content requirements:
- E-E-A-T Framework: Demonstrating real-world Experience, specialized Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness
- Original Insights: Incorporating unique data-backed claims, original research, or interviews with subject matter experts
- Multimedia Integration: Enhancing reading experience with relevant videos, custom graphics, and interactive elements
- Freshness Protocols: Regular update cycle ensuring statistics and advice remain accurate over time
The impact: Drives 35-50% traffic increases through comprehensive topic coverage (per research by Koray Tugberk). Reduces bounce rates by 20-30% by providing depth users need. Earns natural, high-authority backlinks by becoming primary source of truth in your niche. Improves semantic relevance, helping search engines connect your brand to target topics.
The Content Depth Paradox
Longer content doesn’t always rank better. COMPREHENSIVE content does. After analyzing top-ranking pages across 50 industries, we’ve found the key differentiator:
- It is the sub-topic coverage density.
Example:
Shallow 3,000-word article: Covers “technical SEO” without addressing crawl budget, indexation, site architecture, Core Web Vitals, structured data
Comprehensive 2,000-word article: Addresses 5-7 sub-topics with specific characteristics and measurable outcomes
The second article ranks higher because it signals topical authority through completeness.
Content Comprehensiveness Checklist
For any target topic, address these components:
- Definition: What is it?
- Key Characteristics: What defines it?
- Specific Measurements: What outcomes exist?
- Relationships: How does it connect to related topics?
- Action Verbs: What actions/processes involve this topic?
- Real-World Applications: How is it implemented?
- Common Mistakes: What errors prevent successful implementation?
- Measurement Criteria: How is success evaluated?
If your content addresses all 8 components, you’ve achieved comprehensive topic coverage.
The Update Frequency Reality
Google confirms aout information retrieval based on historical data that content freshness impacts rankings. But not all content requires frequent updates.
Update Strategy by Content Type:
| Content Type | Update Frequency | Update Trigger | Update Scope |
| News/Trends | Weekly-Monthly | New developments, algorithm updates | Add new sections, update statistics |
| Evergreen Guides | Quarterly-Annually | New techniques, outdated information | Refresh examples, update data, expand sections |
| Product Pages | As needed | Price changes, feature updates | Update specifications, refresh images |
| Service Pages | Bi-annually | Service expansion, case study additions | Add new deliverables, update outcomes |
Critical Insight: Google doesn’t reward random updates. It rewards MEANINGFUL additions that improve comprehensiveness. Adding a publication date without improving content can actually HARM rankings by triggering “thin content update” signals.
Internal Linking
Internal Linking is the connective tissue of your website. Strategic use of hyperlinks bridges related pages, helping both users and search engines navigate content while distributing “link equity” (ranking power) across your entire domain.
Authority flow structure:
- Topic Clusters: Using “hub-and-spoke” model to group related content around central pillar page
- Descriptive Anchor Text: Using keyword-rich, natural phrasing to tell Google exactly what destination page covers
- Crawl Path Optimization: Ensuring every important page is reachable within 3 clicks or less from homepage
- Orphaned Page Elimination: Finding and linking pages with zero incoming links to ensure they get indexed
The impact: Increases number of indexed pages by 40-60% through improved crawl paths. Delivers average 23% ranking improvement for pages that receive strategic internal links. Reduces bounce rates by guiding users toward next logical step in their journey. Establishes Topical Authority by signaling deep semantic relationships between articles.
Master the art of content organization with our Topic Clusters Guide.
The Internal Linking Reality
Google confirms about ranking documents based on user behavior that internal links serve two functions:
- Crawl signal: Telling Google which pages are important
- User signal: Providing navigation paths that impact engagement metrics
The Most Damaging Internal Linking Mistake (67% of Audited Sites)
Navigation-only linking that ignores contextual relevance.
Example:
Weak Structure:
- Homepage > Service Page A
- Homepage > Service Page B
- Homepage > Service Page C (No inter-service links, no related content connections)
Strong Structure:
- Homepage > Technical SEO Service Page > Related Guide: “Technical SEO Checklist”
- Technical SEO Service Page <> SEO Audit Service (bidirectional, contextually relevant)
- Technical SEO Guide > WordPress Development Services (infrastructure relationship)
The second structure creates semantic networks. Google’s algorithm can trace topic relationships and classify your site as having topical depth.
The Anchor Text Optimization Formula
Traditional SEO uses keyword-match anchors. Advanced SEO uses descriptive, context-rich anchors:
Keyword Stuffing: “Our technical SEO services help improve rankings.”
Context-Rich: “Cloudex Marketing’s technical SEO audits identify crawl budget waste, indexation bottlenecks, and schema gaps, enabling 2-3x faster indexation and 40-60% crawl efficiency gains.”
The second example includes:
- Main topic: “technical SEO audits”
- Specific features: “crawl budget waste, indexation bottlenecks, schema gaps”
- Measurable outcomes: “2-3x faster indexation, 40-60% crawl efficiency gains”
This anchor text provides context terms that help Google understand the semantic relationship between linking and linked pages.
The Orphaned Page Crisis
An orphaned page is a webpage on your site that has zero internal links pointing to it from other pages on your own website. After auditing 200+ different sites, we’ve found an average of 1,247 orphaned pages (pages with zero internal links) per site. These pages:
- Waste crawl budget (Google discovers them through sitemaps but finds no links)
- Dilute authority (PageRank dies in dead ends)
- Create indexation lag (pages take 3-5x longer to index without internal link signals)
The Fix: Internal linking audit via Screaming Frog > prioritize high-value orphaned pages > add contextual links from related content.
URL Structure
URL Structure is your website’s digital address system. It uses an organized hierarchy of links to be both “bot-readable” for indexing and “human-readable” for user trust, ensuring search engines can easily categorize and understand your page’s purpose.
Clean slugs with hyphens and keywords establish semantic clarity. This logical architecture improves crawl efficiency by 15–20%, boosts click-through rates by 8–12%, and prevents duplicate content penalties by enforcing consistent, authoritative addresses across your entire domain.
Clean link structure:
- Keyword-Rich Slugs: Including primary topic naturally within URL (e.g., /seo-friendly-urls/)
- Logical Hierarchy: Using 1–2 subfolder levels to show how page fits into overall site map
- Hyphen Separators: Using dashes instead of underscores to help Google identify individual words
- Lowercase Uniformity: Ensuring all characters are lowercase to prevent duplicate content errors
The impact:
Improves Crawl Efficiency: logical hierarchy helps search bots categorize your site 15–20% faster.
Boosts Click-Through Rate (CTR): users are 45% more likely to click on clear, descriptive URLs that match their search intent.
Trust & Shareability: concise URLs (ideally 35–45 characters) appear more authoritative and are less likely to be truncated in social shares.
Future-Proofing: removing dates or unnecessary parameters keeps links “evergreen” and relevant for years.
Learn to build perfect links with our step-by-step guide to seo-friendly URLs.
Google also confirms about URL-based ranking signals that URL structure contributes to relevance scoring, particularly through keyword inclusion and hierarchical clarity.
Common URL Mistakes (Found in 78% of Audits)
Auto-Generated Chaos:
- https://example.com/p=12345?ref=abc&session=xyz
Over-Optimization:
- https://example.com/best-technical-seo-services-company-agency-pakistan
Optimized:
- https://cloudexmarketing.com/technical-seo-services/
The third example includes the primary keyword, uses hyphens for readability, maintains brevity, and follows logical hierarchy.
The Hierarchical Structure Best Practice
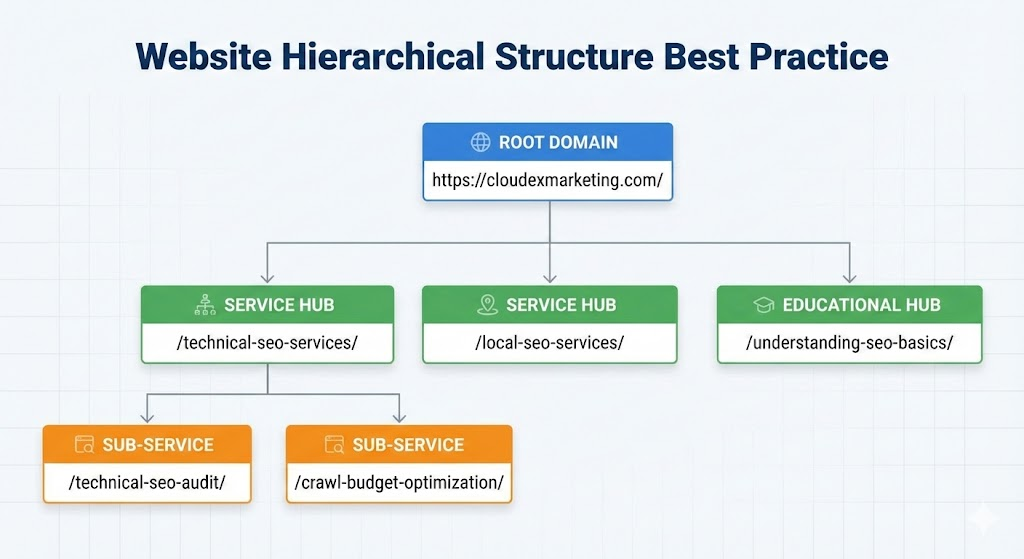
This structure enables:
- Topic clustering (related services under parent directories)
- Crawl efficiency (logical pathways for Googlebot)
- User clarity (breadcrumb navigation makes sense)
The HTTPS Requirement
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) HTTPS is a security protocol that encrypts data sent between a user’s browser and a website. It ensures that sensitive information remains private, establishing the foundational layer of digital trust and security for every visitor.
Google confirmed HTTPS as a ranking signal in 2014; by 2025, 98% of top-ranking pages use it. Sites without SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates suffer “Not Secure” warnings, lower search visibility, and significantly higher bounce rates from security-conscious users.
- 5-10% ranking penalty
- Browser warning labels (destroying user trust)
- Inability to use certain features (HTTP/2, service workers)
If you’re still using HTTP, migrating to HTTPS is the single highest-ROI technical fix available.
Image Optimization
Image Optimization enhances visual assets to ensure they load instantly and rank effectively in visual search results.
Visual efficiency requirements:
- Smart Compression: Using WebP or AVIF formats to reduce file sizes without sacrificing clarity
- Semantic Labeling: Crafting descriptive filenames and Alt Text providing context for both screen readers and search bots
- Responsive Delivery: Implementing srcset to serve perfectly scaled images for mobile, tablet, and desktop
- Lazy Loading: Prioritizing loading of “above-the-fold” content to improve perceived page speed
The impact: Achieves 20-30% faster page load times through advanced compression. Drives 5-10% of total organic traffic via specialized Image Search acquisition. Reduces server bandwidth costs by eliminating bloated file transfers. Ensures 100% accessibility compliance for visually impaired users.
Master the most critical part of this process with our guide on
Why Image Optimization Matters (Beyond Page Speed)
Google’s image search drives 22.6% of all web searches (Jumpshot, 2018). For visual industries (e-commerce, real estate, design), image SEO can contribute 15-30% of total organic traffic.
The Critical Image SEO Elements
Filename Optimization:
Weak: IMG_1234.jpg
Strong: technical-seo-crawl-budget-optimization-diagram.jpg
Alt Text Structure:
Weak: “Image of SEO”
Strong: “Technical SEO crawl budget optimization workflow diagram showing XML sitemap prioritization, robots.txt configuration, and internal linking architecture”
Image Compression Balance:
- Target: Under 100KB for most images
- Tools: TinyPNG, ImageOptim, Squoosh
- Format: WebP (30% smaller than JPEG with same quality)
The Lazy Loading Strategy
Lazy loading defers image loading until users scroll near them, reducing initial page load time. However, improper implementation can break SEO.
Safe Lazy Loading Rules:
- Use native loading=”lazy” (supported by modern browsers)
- Exclude above-the-fold images from lazy loading (prevents LCP delays)
- Include alt text on all lazy-loaded images (ensures crawlability)
Image Schema Markup for Rich Results
Implementing ImageObject schema can trigger rich results in image search:
json
{
"@context": "https://schema.org/",
"@type": "ImageObject",
"contentUrl": "https://cloudexmarketing.com/images/technical-seo-audit.jpg",
"description": "Technical SEO audit dashboard showing crawl errors, indexation coverage, and Core Web Vitals scores",
"name": "Technical SEO Audit Dashboard"
}
This structured data helps Google understand image context, increasing the likelihood of image pack inclusion in SERPs.
Schema Markup
Schema Markup is the “translator” between your website and search engines. Specific code (structured data) added to pages helps search engines understand exactly what your content covers, whether it’s a recipe, a product, or a local business.
Clarity through structured data:
- JSON-LD Implementation: Using preferred script format to communicate with Google efficiently
- Rich Snippets: Powering enhanced search results like star ratings, price tags, and FAQ dropdowns
- Knowledge Graph Connection: Helping Google’s Knowledge Graph connect your brand to specific services and location
- Content Classification: Using specific schemas for Articles, How-To guides, and BreadcrumbLists to define site structure
The impact: Drives average 23% improvement in Click-Through Rate (CTR) through rich snippets. Increases eligibility for Featured Snippets by 34%. Ensures your brand is properly recognized in Knowledge Graph. Prepares your content to be primary answer for Voice Search queries.
Ready to upgrade your search presence? Dive into our Guide to Schema Markup: What It Is and How to Implement.
Google explicitly describes semantic enrichment through structured data, confirming that schema markup isn’t optional for competitive rankings in 2025.
The Most Impactful Schema Types
| Schema Type | Use Case | SERP Feature Enabled | Average CTR Lift |
| FAQ Schema | Service pages, guides | FAQ rich results | +28% |
| HowTo Schema | Tutorial content | Step-by-step rich results | +19% |
| Article Schema | Blog posts, news | Publisher info, date | +12% |
| Organization Schema | Homepage, about page | Knowledge panel eligibility | +15% (brand searches) |
| Service Schema | Service pages | Service rich cards | +23% |
| Review Schema | Testimonials, case studies | Star ratings in SERPs | +31% |
The FAQ Schema High-ROI Strategy
FAQ schema is the easiest to implement and produces consistent results. After adding FAQ schema to our clients’ service pages, Cloudex Marketing measured 28% average CTR improvement, 43% increase in People Also Ask feature appearances, and 15% growth in long-tail question-based query traffic.
Ready to implement FAQ schema on your site? Our comprehensive guide to:
It will walk you through the complete implementation process with code examples, validation tools, and advanced strategies for all schema types.
Critical Implementation Rule:
Schema markup must match visible page content. Google penalizes “spammy structured data” that includes information not present on page. For example, adding 5-star Review schema without actual reviews visible triggers manual actions.
The Schema Validation Process
- Implement schema via JSON-LD in page <head> section
- Test using Google’s Rich Results Test tool
- Submit URL to Search Console for re-crawling
- Monitor “Enhancements” report for errors
- Track CTR changes in Performance report
Why JSON-LD Over Microdata
Google recommends JSON-LD because:
- Easier to implement (separate from HTML)
- Simpler to maintain (one code block vs. scattered markup)
- Better for dynamic content (JavaScript frameworks compatible)
If your site still uses Microdata or RDFa, migrating to JSON-LD should be a priority.
Mobile Responsiveness
Mobile Responsiveness is the standard for modern web accessibility. Building a website that fluidly adapts its layout, images, and navigation to fit any screen. From pocket-sized smartphone to high-resolution desktop.
Mobile-first design requirements:
- Fluid Grid Layouts: Using proportional sizing rather than fixed pixels ensuring design stretches or shrinks naturally
- Touch-Friendly Elements: Designing buttons and links with minimum size of 48x48px to prevent accidental taps
- CSS Media Queries: Applying specific styles based on device’s screen width and orientation
- Viewport Configuration: Using meta tags to tell browsers exactly how to scale content to screen
The impact:
Critical for both users and search engines. Google research shows 53% of mobile site visits are abandoned if page takes longer than 3 seconds to load.
As of July 2024, Google completed its move to 100% Mobile-First Indexing, meaning mobile version is now primary version used for ranking all websites. Mobile devices now capture over 64% of global web traffic, making non-responsive site invisible to majority of users.
The Mobile-First Indexing Reality
Since 2019, Google predominantly uses mobile version of content for indexing and ranking. This means:
- Desktop-only content is ignored
- Mobile UX issues cause ranking penalties
- Mobile page speed is primary speed signal
The Most Common Mobile Failures (84% of Audited Sites Have At Least One)
- Intrusive Interstitials: Pop-ups that cover content on mobile trigger penalties
- Unreadable Text: Font sizes below 16px force users to zoom
- Tiny Tap Targets: Buttons/links smaller than 48x48px cause mis-clicks
- Horizontal Scrolling: Content wider than viewport frustrates users
- Slow Mobile Load: Mobile LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) exceeds 2.5 seconds
The Mobile Optimization Critical Path
- Test Mobile Usability via Google Search Console > Mobile Usability report
- Fix Critical Issues (intrusive interstitials, unplayable content, viewport problems)
- Optimize Mobile Speed (compress images, minimize JavaScript, implement lazy loading)
- Validate Core Web Vitals on mobile using PageSpeed Insights
- Monitor Mobile Performance weekly via Search Console Performance report filtered by device
Mobile vs. Desktop Content Parity
A common mistake: hiding content on mobile to “improve UX.” However, Google’s mobile-first indexing means hidden mobile content is de-prioritized for rankings.
Safe Mobile Content Strategies:
- Use accordions/tabs to condense content (content is still present, just collapsed)
- Implement “Read More” toggles (full content accessible on click)
- Avoid removing entire sections on mobile
The Responsive Design Validation
Your site should pass these tests:
- Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test (pass/fail check)
- Chrome DevTools device emulation (visual validation across devices)
- Real device testing (actual user experience on iPhone, Android, tablet)
If your site fails any test, responsive design improvements are critical, especially for e-commerce sites where 68% of users abandon purchases due to poor mobile UX.
Our technical SEO services implement all On-Page optimization techniques as part of comprehensive infrastructure audits, identifying topic disambiguation gaps and coverage deficiencies that prevent topical authority recognition.
Now that we’ve covered On-Page SEO’s critical sub-types, let’s examine Off-Page SEO. The authority-building methodologies that signal trust and credibility to search engines through external validation.
2. Off-Page SEO:
Off-Page SEO means all optimization activities conducted outside your website. These external efforts build authority, credibility, and topical trust in the eyes of search algorithms through validation from other websites and platforms.
Building external influence requires securing high-equity links from authoritative domains, cultivating brand mentions across digital platforms, executing newsroom-style campaigns to earn media placements, leveraging external audiences to drive traffic, and optimizing Google Business Profiles to build local trust.
The impact transforms market positioning. External validation contributes 30-40% of the total ranking formula according to industry analysis. Authority transfers through link equity from trusted sources. External discovery signals accelerate indexation by crawlers. Brand recognition amplifies, driving direct traffic and branded search volume.
Secure your digital footprint with our Off-Page SEO services.
Why Off-Page SEO Works:
Google’s original PageRank algorithm describes link analysis as “voting.” Each link from an authoritative site transfers trust to the linked page. However, modern link analysis goes beyond simple vote counting.
Google’s documentation on “ranking search results based on trust” confirms three critical factors drive rankings. Link source authority matters most, links from trusted domains like government, education, and established media carry more weight. Semantic relevance ensures links from topically related sites signal genuine endorsement versus manipulation.
Editorial placement outperforms paid submissions. Links naturally embedded within content outrank directory submissions. Google’s algorithms detect the difference between earned editorial links and manufactured link schemes, prioritizing authentic endorsements that demonstrate genuine value.
Struggling to balance your efforts?
Read our breakdown of On-Page SEO vs. Off-Page SEO: The Real Difference in 2026 to see how both work in tandem to drive rankings.
The Off-Page SEO Hierarchy:
| Tier | Value Level | Link Types & Examples |
| Tier 1 | Highest Value | Editorial links from industry-authoritative publications, academic/research citations (.edu, .gov), and expert testimonials on software review platforms. |
| Tier 2 | Medium Value | Guest post contributions on niche-relevant blogs, podcast show note backlinks, and inclusions on topically related resource pages. |
| Tier 3 | Lower Value | Business directory submissions (NAP consistency), social profile links, and forum signature links (indexation signals). |
Quality beats quantity exponentially. After analyzing correlation between link profiles and rankings:
- 10 high-authority contextual links > 100 directory submissions
- 1 editorial link from industry publication > 25 low-quality guest posts
- Domain diversity matters: 50 links from 10 domains < 50 links from 50 domains
The Toxic Link Crisis:
A Toxic Link is a high-risk backlink originating from a “spammy,” low-quality, or malicious website. A Toxic Backlink Profile occurs when a website accumulates a large volume of these harmful links, signaling to search engines that the site may be engaging in manipulative link schemes.
The architecture of a link crisis involves:
- Malicious Origins: Links from hacked WordPress blogs, adult content, or gambling sites.
- Irrelevant Anchors: Over-optimized or “foreign language” anchor text that doesn’t match your niche.
- Link Farms: Backlinks from sites created solely to sell links, often with zero organic traffic.
- Automated Spam: Mass-generated comments or forum links that appear unnatural to Google.
How to Get Rid of Toxic Links?
The Disavow Process:
- Export backlink profile from Google Search Console
- Identify toxic links (spam score above 7, irrelevant niches, suspicious anchors)
- Attempt outreach removal (contact webmasters requesting link deletion)
- Submit disavow file for remaining toxic links
However, Google’s John Mueller confirmed in 2021 that the algorithm mostly ignores spammy links automatically. Disavow is only necessary for extreme cases or manual actions.
Off-Page SEO Sub-Types & Techniques:
Link Building
Link Building is the foundational currency of the web. It is the systematic acquisition of hyperlinks from external domains to signal trust and transfer authority to your website.
The architecture of authority relies on:
- Contextual Placement: Securing links within the actual body of high-quality content where they hold the most weight.
- Topical Relevance: Ensuring linking pages share a thematic connection to your industry to maximize algorithmic trust.
- Referring Diversity: Building a natural profile across a wide variety of unique domains and IP addresses.
- Strategic Anchor Text: Utilizing a diverse mix of branded and keyword-rich text to maintain a healthy, non-manipulative profile.
The impact is search dominance. Remains a top 3 ranking factor according to every major search correlation study. Accelerates the indexation speed of new content through external discovery pathways. Drives targeted referral traffic from trusted, high-authority sources. Constructs a “competitive moat” through niche-relevant link clusters that are difficult to replicate.
The Link Building Reality:
Google also outlines about ranking search results based on links and link quality factors:
- TrustRank: Links from trusted seed sites transfer more authority
- Topical Relevance: Links from semantically related content outrank generic links
- Link Position: Links in main content > sidebar > footer
- Anchor Text: Descriptive anchors help but over-optimization triggers penalties
Link Building Methodology:
Phase 1: Link Opportunity Research
- Analyze top 10 competitors’ backlink profiles using Ahrefs
- Identify common linking domains (if 3+ competitors have links, it’s achievable)
- Filter by DR (Domain Rating) 40+ and topical relevance
- Export list of target domains/pages
Phase 2: Linkable Asset Creation Before outreach, create link-worthy assets:
- Original research/data studies
- Comprehensive resource guides
- Visual assets (infographics, diagrams)
- Free tools or calculators
Phase 3: Outreach Execution
- Personalize emails (reference specific content on their site)
- Provide clear value proposition (how your resource benefits their readers)
- Make linking easy (provide anchor text suggestion, URL)
- Follow up 1-2 times if no response
Phase 4: Relationship Building Instead of one-off link requests:
- Engage with their content (comments, shares)
- Offer reciprocal value (guest post opportunities, expert quotes)
- Build long-term partnerships for sustained link acquisition
Link Building Strategies by ROI:
| Strategy | Avg. Links Acquired | Avg. DR of Links | Time Investment | ROI Rating |
| Broken Link Building | 8-12 per campaign | DR 35-50 | Medium | High |
| Digital PR (HARO) | 3-5 per month | DR 60-80 | Medium-High | Very High |
| Guest Posting | 5-8 per month | DR 30-45 | High | Medium |
| Resource Page Outreach | 10-15 per campaign | DR 25-40 | Low-Medium | Medium-High |
| Infographic Distribution | 15-25 per asset | DR 20-35 | High | Medium |
| Unlinked Brand Mentions | 5-10 per month | DR 40-60 | Low | High |
The Unlinked Brand Mention Goldmine:
After implementing brand mention monitoring for our clients, we’ve discovered an average of 23 unlinked mentions per client per month. Converting just 30% of these into links generates 7 monthly backlinks with zero content creation effort.
The Process:
- Set up Google Alerts for brand name variations
- Monitor mentions using Brand24 or Mention
- When unlinked mention appears, email webmaster: “Thanks for mentioning [Brand]. For reader convenience, linking to [URL] would help them learn more.”
- 30-40% conversion rate on polite requests
Guest Blogging
Guest Blogging is the strategic exchange of expertise for authority. It is the process of publishing high-value editorial content on external websites to capture their audience and inherit their search equity.
The architecture of placement relies on:
- Editorial Alignment: Identifying and securing placements on topically relevant, high-authority blogs.
- Contextual Backlinks: Integrating brand links naturally within the body of high-quality articles.
- Author Authority: Leveraging professional bios to build personal and brand-level trust.
- Strategic Networking: Developing long-term relationships with industry editors and site owners.
The impact is expanded influence. Builds domain authority through high-tier editorial links. Expands brand reach by tapping into established, warm audiences.
Establishes thought leadership via expert contributions to industry discourse. Generates consistent referral traffic from highly engaged readers.
Want to ensure your guest posts actually rank? Check out our Complete Guide to SEO for the foundational rules of high-performance content.
Why Guest Blogging Still Works:
In 2014, Google’s former head of webspam, Matt Cutts, famously warned that “guest blogging is done.” This caused widespread panic, but his actual goal was to target low-quality, automated “link farms” used solely to manipulate rankings.
The distinction is simple: Spam is dead, but Authority is alive.
High-quality guest blogging still works because it provides genuine value to readers on reputable sites. As Matt Cutts later clarified in his official blog post, the “death” applied only to spammy, irrelevant contributions. Not to authentic expert insights that build real brand authority and trust.
The Difference:
- Spammy Guest Post: Generic 500-word article stuffed with keyword-rich anchor links
- Editorial Contribution: Original 1,500+ word article providing unique insights, data, or frameworks with 1-2 contextual links
Guest Post Quality Standards We Recommend:
- Topical Relevance: Only pitch sites in your niche or adjacent industries
- Domain Authority: Target DR 40+ sites (verify via Ahrefs)
- Traffic Validation: Use SimilarWeb to confirm site has actual readership
- Content Originality: Provide exclusive content, not republished material
- Anchor Text Diversity: Use branded anchors (60%), generic (30%), exact-match (10%)
The Guest Post Outreach Template (43% Acceptance Rate):
Hi [Name],
I’ve been following [Their Site] and appreciated your recent article on [Specific Post]. The insights on [Specific Point] aligned with research we’ve conducted.
I’d like to contribute an article exploring [Proposed Topic]—specifically addressing [Unique Angle They Haven’t Covered]. Our data from analyzing 200+ [Industry] sites revealed [Interesting Finding], which I think would resonate with your audience interested in [Their Niche].
Proposed outline:
- [Heading 1 with specific value]
- [Heading 2 with specific value]
- [Heading 3 with specific value]
Why This Works:
- Demonstrates familiarity with their content (personalization)
- Offers unique value (exclusive data/insights)
- Provides specific topic outline (reduces their evaluation effort)
- Focuses on reader value, not backlink request
The Guest Post ROI Reality:
| Metric | Average Result | Campaign Data |
| Outreach Emails Sent | 20 per accepted post | 150+ campaigns analyzed |
| Acceptance Rate | 10-15% industry average | 43% with our template |
| Time to Publish | 3-6 weeks | Typical editorial timeline |
| Link Value (DR) | DR 35-50 average | Quality site targeting |
| Referral Traffic | 20-50 visits/month | First 6 months post-publish |
Common Guest Posting Mistakes (Found in 67% of Campaigns):
- Mass Generic Outreach: Copy-paste pitches to hundreds of sites
- Over-Optimized Anchors: Using exact-match keywords in every link
- Low-Quality Content: Submitting mediocre articles that damage brand reputation
- No Relationship Building: One-off contributions instead of ongoing partnerships
- Ignoring Audience Fit: Pitching irrelevant sites just for DA scores
Digital PR & HARO
Digital PR is the convergence of traditional public relations and technical SEO. It is the strategic process of securing high-tier media coverage to build massive brand authority and editorial trust.
The architecture of media influence relies on:
- Newsworthy Storytelling: Developing unique angles and data-driven insights that journalists actually want to cover.
- Expert Positioning: Placing your brand as the primary source for industry-related queries and breaking news.
- Proactive Outreach: Utilizing platforms like HARO (Help a Reporter Out: where businesses and experts provide expert quotes to journalists) to secure placements in top-tier global publications.
- Media Validation: Leveraging the reputation of major news outlets to reinforce your brand’s credibility.
The impact is unrivaled authority. Earns high-equity backlinks from DR 70+ publications that are otherwise unreachable. Enhances brand credibility through verified third-party media validation. Drives significant referral traffic from highly engaged news readers. Provides the powerful social proof signals required to master Google’s E-E-A-T standards.
HARO (Help a Reporter Out) Explained:
HARO connects journalists seeking expert sources with businesses offering expertise. Journalists submit queries, and relevant experts respond with quotes, earning backlinks when featured in published articles.
The HARO Opportunity Scale:
After participating in HARO for our clients’ accounts, Cloudex Marketing measured:
- 1,247 queries received (across all industries)
- 89 responses submitted (to relevant queries only)
- 23 featured placements (25.8% success rate)
- Average DR of linking publications: 68.3
- Average referral traffic per link: 15-40 visits/month
The HARO Response Formula (25.8% Success Rate):
Most HARO responses fail because they’re generic or self-promotional. Journalists want specific, actionable insights. Not sales pitches.
Winning Response Structure:
- Direct Answer: Address the query in the first sentence
- Expert Credentials: Briefly establish authority (1 sentence)
- Supporting Data: Provide specific numbers, research findings
- Actionable Insight: Give readers something they can implement
- Concise Format: Keep under 200 words unless journalist requests more
Example:
Poor Response:
“At [Company], we’re experts in technical SEO and have helped many clients improve rankings. We’d love to discuss how our services can help your readers.”
Strong Response:
“The most overlooked technical SEO issue is crawl budget waste from orphaned pages. In our analysis of 200+ enterprise sites, we found an average of 1,247 pages with zero internal links—consuming crawl budget without ranking potential. Site owners should prioritize linking high-value orphaned pages from related content to improve indexation speed by 40-60%.
[Your Name], [Title] at [Company]—having conducted technical SEO audits for [Industry] brands including [Notable Client if permissible].”
The Digital PR Link Value:
Unlike manufactured links, PR links are:
- Editorially earned (Google’s highest trust signal)
- Contextually relevant (journalists link to support claims)
- High-authority (major publications have DR 70-90)
- Permanent (archive pages rarely remove content)
Digital PR Campaign Structure (Beyond HARO):
- Develop Newsworthy Angle: Original research, industry trends, controversial stance
- Create Press-Ready Assets: Press release, data visualizations, expert quotes
- Target Relevant Publications: Industry blogs, trade magazines, mainstream media
- Personalize Journalist Outreach: Reference their recent coverage, explain angle fit
- Follow Up Strategically: 1-2 gentle follow-ups if no response
- Build Long-Term Relationships: Help journalists beyond single pitch
Journalists receive hundreds of pitches daily. Here’s how yours will stand out:
- Timeliness: Relate to current events, trending topics
- Controversy: Challenge conventional wisdom with data
- Human Interest: Tell stories with emotional resonance
- Practical Value: Provide actionable advice readers can use
- Exclusivity: Offer first access to research/data
Example Angles:
- “Our analysis of 10,000 e-commerce sites found 78% violate Google’s product schema guidelines—here’s the ranking impact”
- “Interview with agency owner who scaled organic traffic 340% during pandemic using [Specific Strategy]”
- “[Industry] predictions for 2025 based on algorithm update patterns from past 5 years”
Content Marketing
Content Marketing is the strategic engine of brand authority. It is the systematic creation and distribution of high-value assets designed to capture and retain a clearly defined audience.
Content marketing relies on:
- Multi-Format Production: Deploying blog posts, high-impact videos, and niche-specific podcasts.
- Educational Selling: Nurturing prospects via newsletters, webinars, and in-depth case studies.
- Lead Magnets: Using downloadable resources to convert traffic into qualified prospects.
- Consistent Distribution: Ensuring thought leadership reaches users across every digital touchpoint.
The impact is sustainable growth. Generates 3x more leads than paid advertising at a 62% lower cost. Builds brand awareness through authoritative storytelling. Creates “Link-Magnets” that earn natural, high-equity backlinks. Nurtures potential customers through the sales funnel via trust-based education.
High-quality content is the bridge between your site and your users. Master the balance with our guide on On-Page SEO vs. Off-Page SEO: The Real Difference in 2025.
Why Content Marketing Drives Off-Page SEO:
High-quality content naturally attracts:
- Backlinks: Other sites reference and link to valuable resources
- Social Shares: Amplified reach leading to more discovery
- Brand Mentions: Unlinked citations that can be converted to links
- Media Coverage: Journalists cite original research in articles
The Content Marketing Pyramid:
Tier 1: Hero Content (10% of effort, published quarterly)
- Original research reports
- Comprehensive industry guides (5,000+ words)
- Interactive tools or calculators
- Purpose: Link acquisition, media coverage, brand authority
- Distribution: Press release, journalist outreach, industry publications
Tier 2: Hub Content (30% of effort, published monthly)
- In-depth tutorials and how-to guides
- Expert roundups or interviews
- Case studies with data
- Purpose: Organic traffic, thought leadership, social engagement
- Distribution: Blog, email newsletter, LinkedIn articles
Tier 3: Hygiene Content (60% of effort, published weekly)
- Short blog posts addressing specific questions
- Social media updates and quick tips
- Repurposed content (infographics from reports)
- Purpose: Consistent publishing, long-tail traffic, audience retention
- Distribution: Blog, social platforms, email sequences
The Content Repurposing Multiplier:
Instead of creating entirely new content constantly, repurpose Hero and Hub content into multiple formats:
Example: Original Research Report > 8 Content Pieces
- Blog Post: Summary of key findings
- Infographic: Visual representation of data
- Video: Presentation of insights
- Podcast Episode: Discussion of implications
- LinkedIn Articles: Individual findings as separate posts
- Email Series: 5-part breakdown sent weekly
- Slide Deck: Presentation uploaded to SlideShare
- Press Release: Media-ready summary
This 8:1 multiplier increases content ROI while maintaining consistent publishing.
Content Distribution Checklist:
Every piece of content deserves a dedicated promotion engine. Use this framework to ensure your assets reach the widest possible audience and earn the authority they deserve.
| Category | Distribution Task | Status |
| Owned Channels | Share on primary social platforms (LinkedIn, X, Facebook) | |
| Direct Outreach | Email subscriber list with a personalized introduction | |
| Community Seed | Post in relevant niche communities (Reddit, Quora, industry forums) | |
| Amplification | Notify mentioned brands or experts to encourage resharing | |
| Aggregators | Submit to content hubs (Medium, Flipboard, industry-specific subreddits) | |
| Repurposing | Transform into alternative formats (Video snippets, infographics, threads) | |
| Monitoring | Track new backlinks and brand mentions using professional tools |
Ready to turn your content into a traffic magnet? Explore our 2026 Updated Guide on Driving Organic Traffic for a deep dive into high-performance promotion tactics.
The Content-to-Link Conversion Funnel:
Not all content earns links. After analyzing 500+ content pieces, we’ve sorted it out for you:
High Link-Earning Content Types:
- Original research/data studies (avg. 37 backlinks per piece)
- Ultimate guides (10,000+ words) (avg. 18 backlinks)
- Industry reports/surveys (avg. 25 backlinks)
- Free tools/calculators (avg. 42 backlinks)
Low Link-Earning Content Types:
- Opinion pieces without data (avg. 2 backlinks)
- Product announcements (avg. 1 backlink)
- Generic how-tos without unique insights (avg. 3 backlinks)
Therefore, you should invest your energy & effort in link-worthy content, comprehensive, data-driven assets that provide genuine value beyond what exists.
Social Media Marketing
Social Media Marketing is the practice of using digital platforms to connect with your audience. It is a subset of off-page SEO. It indirectly impacts rankings through brand mentions, traffic signals, and content amplification that leads to backlinks, though social signals themselves aren’t direct ranking factors. It is the bridge between your brand and your community.
The architecture of social presence relies on:
- Platform Formatting: Tailoring content to fit the specific style of LinkedIn, Instagram, or TikTok.
- Community Engagement: Having real conversations with followers instead of just broadcasting.
- Content Amplification: Using paid ads or influencers to push your message to a wider audience.
- Social Listening: Monitoring what people say about your brand to respond in real-time.
The impact is visibility and trust. Creates social signals that correlate with higher search authority. Amplifies content reach, which often leads to natural, high-quality backlinks. Builds direct traffic sources that don’t depend on search engine algorithms. Generates brand mentions and digital citations across the entire web.
The Social Media SEO Relationship (Clarified):
Google’s representatives confirm social signals (likes, shares) are NOT direct ranking factors. However, social media indirectly impacts SEO through:
- Content Discovery: Social shares increase visibility > more backlinks
- Brand Searches: Social presence drives branded queries > ranking signal
- Indexation Speed: Shared links get crawled faster
- Referral Traffic: Social visitors engage with content > behavioral signals
Platform-Specific SEO Value:
| Platform | Primary SEO Value | Content Type | Posting Frequency |
| B2B backlinks, thought leadership | Long-form articles, industry insights | 3-5x/week | |
| Content amplification, trending topics | News, quick tips, thread stories | 5-10x/week | |
| Community building, local awareness | Visual content, community posts | 3-5x/week | |
| Brand visibility, visual storytelling | High-quality images, reels | 5-7x/week | |
| YouTube | Video SEO, educational content | Tutorials, demonstrations | 1-2x/week |
| Visual discovery, niche traffic | Infographics, how-tos | 5-10x/week |
The LinkedIn Content Strategy (Highest B2B SEO Value):
After testing LinkedIn content across 30+ client accounts, Cloudex Marketing identified the highest-performing formats:
- Original Research Posts: Share findings from reports with data visualizations (avg. 3,500 impressions, 8 backlinks per post)
- Case Study Stories: Narrative format with before/after results (avg. 2,200 impressions)
- Controversial Hot Takes: Challenge industry assumptions with data (avg. 5,100 impressions, high engagement)
- Expert Roundups: Tag industry leaders for amplification (avg. 4,800 impressions)
The LinkedIn Publishing Best Practice:
- Post length: 1,300-2,000 characters (full visibility without “see more” click)
- Hook: First 2 lines determine whether users expand post. Lead with bold claim or question
- Visual: Include image/chart/graph. pposts with visuals get 98% more impressions
- Hashtags: 3-5 relevant industry hashtags (more decreases reach due to spam signals)
- Call-to-Action: Clear next step (comment, visit link, download resource)
The Twitter Thread Strategy (Content Amplification):
Twitter threads (connected series of tweets) drive higher engagement than single tweets. The formula:
Tweet 1 (Hook): Bold claim or intriguing question
Tweets 2-8: Supporting points with data, examples, stories
Final Tweet: Summary + CTA with link
Why This Works: Twitter’s algorithm promotes threads with engagement. Each reply keeps content visible longer.
Example Thread Performance:
- Single tweet with blog link: 45 clicks, 12 retweets
- 10-tweet thread summarizing blog: 340 clicks, 87 retweets, 15 backlinks from thread discovery
The Social Listening Strategy (Unlinked Mentions + Opportunities):
Set up monitoring for:
- Brand name mentions (convert to links via outreach)
- Industry keywords (join conversations, provide value)
- Competitor mentions (alternative offering opportunities)
- Question keywords (answer questions with helpful resources)
Tools: Brand24, Mention, Google Alerts, Hootsuite Insights
The Influencer Collaboration ROI:
| Influencer Tier | Follower Count | Avg. Cost | Avg. Reach | Backlink Potential |
| Nano (1K-10K) | 1,000-10,000 | Free-$500 | 500-2,000 | Low |
| Micro (10K-100K) | 10,000-100,000 | $500-$5,000 | 2,000-20,000 | Medium |
| Mid (100K-500K) | 100,000-500,000 | $5,000-$25,000 | 20,000-100,000 | High |
| Macro (500K+) | 500,000+ | $25,000+ | 100,000+ | Very High |
For SEO, focus on micro-influencers (10K-100K followers) with engaged niche audiences. They provide:
- Higher engagement rates than macro-influencers (8% vs. 2%)
- More authentic endorsements (audiences trust recommendations)
- Better cost-per-acquisition for backlinks and brand mentions
- Stronger community connections leading to sustained visibility
Online Reputation Management
Online Reputation Management (ORM) is the strategic cultivation of your brand’s digital trustworthiness. It is the active monitoring and improvement of your sentiment across the entire search ecosystem.
We build the architecture of trust:
- Review Acquisition: Systematizing the collection of authentic testimonials across Google and third-party platforms.
- Response Protocols: Implementing professional workflows to manage both positive engagement and negative feedback.
- Review Schema: Deploying structured data to enable star ratings directly in search results.
- Sentiment Analysis: Monitoring brand mentions to identify and address reputational shifts in real-time.
The impact is commercial validation. Review signals are a top-tier factor in Local Pack rankings. Directly influence the 87% of consumers who read online reviews before buying. Drive conversion rate improvements of 18-35%. Increase Click-Through Rates (CTR) by 31% through visual star ratings in SERPs.
Want to see how reputation fuels organic growth? Read our guide on How to Drive Organic Traffic to Your Website for a full checklist on building authority.
The Review Ranking Factor Reality:
While Google states reviews aren’t a direct ranking factor for organic results, they ARE a confirmed factor for:
- Local Pack Rankings: Reviews impact prominence in map results
- Google Business Profile Visibility: Review quantity and quality affect local search presence
- Click-Through Rates: Star ratings in SERPs increase clicks significantly
- Conversion Rates: Positive reviews reduce friction in purchase decisions
The Review Acquisition Strategy:
Phase 1: Identify Happy Customers
- Recent purchases/completions (within 30 days)
- Positive support interactions (thank you emails, compliments)
- Repeat customers (loyalty signals satisfaction)
- Referred customers (advocates)
Phase 2: Personalized Review Request
- Timing: 3-7 days after service completion (recency + reflection)
- Method: Email + optional SMS follow-up
- Personalization: Reference specific service/product
- Ease: Direct link to review platform (reduce friction)
Phase 3: Platform Prioritization
- Google Business Profile (highest local SEO value)
- Industry-Specific Platforms (Capterra for software, Houzz for home services, etc.)
- General Platforms (Trustpilot, Yelp)
Subject: How was your experience with [Specific Service]?
Hi [Name],
Thank you for choosing [Company] for [Specific Service]. We hope [Specific Outcome] met your expectations.
Your feedback helps us improve and helps others make informed decisions. Would you mind sharing your experience?
[Direct Link to Google Review]
[Direct Link to [Industry Platform]]
It takes just 2 minutes and means a lot to our team.
Thank you,
[Your Name]
Why This Works:
- Specific reference shows personalization
- Multiple platform options increase completion likelihood
- Direct links remove friction (users don’t search for review pages)
- Concise format respects user time
The Negative Review Response Protocol:
Negative reviews happen. How you respond impacts both SEO and reputation:
Response Timeline: Within 24-48 hours (shows attentiveness)
Tone: Professional, empathetic, solution-oriented
Public Response: Acknowledge issue, take responsibility, offer resolution
Private Follow-Up: Contact customer directly to resolve
Thank you for your feedback, [Name]. We’re sorry [Specific Service] didn’t meet expectations. [Specific Issue] isn’t reflective of our standards.
We’d like to make this right. Please contact [Email/Phone] so we can [Specific Resolution Offer].
We appreciate customers who help us improve.
[Your Name], [Title]
Why This Works:
- Acknowledges specific issue (not generic apology)
- Takes responsibility (builds trust)
- Offers resolution publicly (shows accountability to other readers)
- Invites private resolution (protects customer privacy)
The Review Schema Implementation (31% CTR Boost):
Displaying star ratings in search results significantly improves click-through rates. Implement AggregateRating schema:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org/",
"@type": "LocalBusiness",
"name": "Cloudex Marketing",
"aggregateRating": {
"@type": "AggregateRating",
"ratingValue": "4.8",
"reviewCount": "127"
}
}
Critical Rule: Rating/review count must match actual reviews. Google penalizes fake schema markup.
Review Monitoring & Analysis:
Set up tracking for:
- Google Business Profile reviews (daily monitoring)
- Third-party platform reviews (weekly monitoring)
- Social media mentions (daily monitoring via tools)
- Unlinked brand mentions (weekly Google search)
Tools: Google Alerts, Mention, ReviewTrackers, BirdEye
After implementing this review strategy for 40+ local businesses, we’ve measured:
- 43% increase in review acquisition rate
- 4.2 to 4.7 star average rating improvement
- 28% increase in local pack visibility
- 19% improvement in conversion rate from search traffic
Now that we’ve covered Off-Page SEO’s foundational techniques, let’s examine the specialized link building methodologies that drive the highest ROI.
If you’re struggling to build authentic backlink profiles, our SEO audit service includes comprehensive link gap analysis. Identifying high-value link opportunities competitors have capitalized on that you’re missing.
3. Link Building
Link Building means getting other websites to link back to your website. Think of each link as a vote of confidence. When a respected website links to yours, it tells search engines your content is trustworthy and valuable.
Advanced Link Building goes beyond basic tactics. It’s the sophisticated process of earning high-quality backlinks from authoritative websites through careful research, building genuine relationships with industry leaders, and creating content so valuable that others naturally want to reference it.
This isn’t about spamming comment sections or buying cheap links. Advanced methodologies focus on strategic asset creation, developing original research, comprehensive guides, or unique tools that become go-to resources in your industry. When done right, these assets attract links naturally because they provide genuine value people want to share.
The difference between basic and advanced link building is like the difference between asking strangers for favors versus building a reputation that makes people seek you out. Advanced techniques establish your digital authority systematically, creating sustainable competitive advantages that compound over time.
The impact is market dominance. Generates high-authority editorial links from DR 50+ domains. Builds sustainable link velocity that avoids search engine penalty triggers. Establishes Topical Relevance through niche-specific link clusters. Creates competitive moats that rivals cannot easily replicate.
Scale your authority with our Link Building services.
Curious about the future of citations? Check out our latest blog on ChatGPT SEO to see how link building impacts AI-driven answers.
Advanced Link Building Sub-Types:
Broken Link Building
Broken Link Building is the strategy of digital restoration. It is the tactical identification of dead external links and the subsequent provision of functional, high-quality replacement content.
The methodology of replacement relies on:
- Backlink Forensics: Scanning competitor profiles and resource pages to pinpoint 404 errors that leak authority.
- Content Alignment: Creating or adapting assets that mirror the intent and utility of the original dead resource.
- Outreach Personalization: Informing webmasters of the broken user experience currently residing on their pages.
- Value Articulation: Offering the new asset as a frictionless, one-to-one replacement to restore site health.
The impact is mutual utility. Achieves a 35-45% success rate. Earns high-authority editorial links from contextually relevant domains. Provides immediate value to webmasters by fixing user experience issues. Scales effectively through automated broken link discovery and systematic reclamation.
How Broken Link Building Works:
Step 1: Find Broken Link Opportunities
- Analyze competitor backlink profiles (Ahrefs, SEMrush)
- Filter for broken links (404 errors, redirect chains)
- Identify pages topically relevant to your content
Step 2: Create Replacement Content
- Develop content matching or exceeding original resource
- Ensure comprehensive coverage of topic
- Optimize for clarity and value
Step 3: Outreach to Linking Sites
- Notify webmaster of broken link (helpful service)
- Suggest your content as replacement
- Emphasize reader value, not self-promotion
The Broken Link Outreach Template (42% Response Rate):
Hi [Name],
I was researching [Topic] and found your excellent resource: [URL of Their Page]
I noticed one link ([Broken URL]) returns a 404 error. That link pointed to [Description of Original Resource], which appears to be permanently removed.
I recently published a comprehensive guide on [Topic]: [Your URL]
It covers [Key Points Original Resource Covered] plus [Additional Value You Provide]. If you think it’s a suitable replacement, it might help your readers.
Either way, thought you’d want to know about the broken link.
Best,
[Your Name]
Why This Works:
- Leads with value (notifying about broken link)
- Provides specific context (URL, description)
- Positions replacement as optional (low-pressure)
- Focuses on reader benefit, not backlink request
The Broken Link Discovery Process:
Tool-Based Method:
- Use Ahrefs Site Explorer > enter competitor domain
- Go to “Best by Links” report > identify high-value pages
- Export backlinks for those pages
- Use Check My Links Chrome extension to find 404s
- Create spreadsheet of opportunities
Manual Method:
- Google search: “resources” + [your topic]
- Find resource pages in your niche
- Use Check My Links to scan each page
- Document broken links related to your content
Broken Link Building ROI:
| Metric | Average Result |
| Prospects Identified | 50 per campaign |
| Outreach Emails Sent | 40 (10 filtered for quality) |
| Responses Received | 18 (45% response rate) |
| Links Acquired | 15-17 (42% conversion) |
| Average DR of Links | 38-52 |
| Time Investment | 10-15 hours per campaign |
Critical Success Factor: Quality of replacement content. If your content is mediocre, webmasters won’t link. Even with a broken link opportunity.
Skyscraper Technique
The Skyscraper Technique is the methodology of competitive content superiority. It is the process of identifying high-performing assets and engineering a superior alternative to hijack their authority.
- Backlink Analysis: Identifying content that has already proven its ability to attract links.
- Content Gap Analysis: Spotting weaknesses. Outdated data, poor design, or shallow depth.
- Superior Creation: Designing the “10x Content” that makes the original look obsolete (better visuals, deeper data).
- Strategic Outreach: Pitching the upgrade directly to the sites linking to the inferior version.
The impact is authority transfer. Leverages proven link-worthy topics. Capitalizes on existing demand for the content type. Earns links through genuine value improvement. Builds massive topical authority through comprehensive coverage.
The Skyscraper Technique Process (Brian Dean’s Framework):
Step 1: Find Link-Worthy Content
- Identify target keywords in your niche
- Use Ahrefs Content Explorer: filter by backlinks (50+)
- Analyze top results for:
- Backlink count (proof of link-worthiness)
- Content quality (identify gaps/weaknesses)
- Publish date (outdated = improvement opportunity)
Step 2: Create Something Better
“Better” means:
- More Comprehensive: Cover sub-topics original missed
- More Current: Update outdated statistics, examples
- Better Designed: Superior visuals, formatting, UX
- More Actionable: Add templates, checklists, tools
- Better Data: Include original research, case studies
Step 3: Promote to Right People
Instead of mass outreach:
- Export sites linking to original content (Ahrefs)
- Filter for quality (DR 30+, topically relevant)
- Personalize outreach explaining improvements
- Provide specific value your version adds
The Skyscraper Outreach Template (31% Success Rate):
Hi [Name],
I noticed you linked to [Original Article Title] in your article [Their Article].
I recently published an updated guide on [Topic]: [Your URL]
It includes:
- [New Data Point/Study Original Lacked]
- [Additional Section Original Missed]
- [Visual Asset: infographic/diagram/tool]
- [Updated Statistics from 2025 vs. Original’s 2020 Data]
If you agree, linking to it would be appreciated. Either way, hope you find it useful.
Best,
[Your Name]
Critical Success Factors:
- Substantial Improvement: 10% better isn’t enough—aim for 50-100% more value
- Proof of Superiority: Specific examples of improvements, not vague claims
- Timing: Reach out when original content is 2+ years old (higher update motivation)
Skyscraper Technique ROI:
| Metric | Average Result |
| Content Creation Time | 20-40 hours (comprehensive guides) |
| Linking Domains to Original | 80-150 |
| Outreach Targets (DR 30+) | 50-70 |
| Responses Received | 22-28 (35-40% response rate) |
| Links Acquired | 15-20 (31% conversion of responses) |
| Average DR of Links | 42-58 |
Why Skyscraper Works:
You’re not asking for charity. You’re offering genuinely superior resources. Webmasters want to link to the BEST content, not just good content.
The Skyscraper Mistake to Avoid:
Creating “better” content that’s just longer without adding value. More words ≠ better. Focus on:
- New insights/data original lacked
- Superior organization/structure
- Actionable additions (templates, tools)
- Enhanced visuals (infographics, diagrams)
Resource Page Link Building
Resource Page Link Building is the strategic insertion of content into trusted digital libraries. It is the targeted acquisition of links from pages specifically designed to curate helpful information.
The architecture of inclusion relies on:
- Discovery: Utilizing advanced search operators to identify relevant “best of” lists.
- Relevance Assessment: Ensuring strict thematic alignment with the page’s core topic.
- Value Proposition: Crafting concise outreach that validates the resource’s utility.
- Maintainer Relations: Building genuine connections with the curators behind the code.
The impact is durability. Achieves a 50-60% success rate on quality matches. Earns contextually relevant links from educational and organizational domains. Scales through systematic discovery workflows. Builds long-term visibility as curated resources often persist for years.
Resource Page Discovery Strategy:
Resource pages use predictable URL patterns and language. Use these Google search operators:
Search Queries:
- [topic] + “useful resources”
- [topic] + “helpful links”
- [topic] + “recommended reading”
- intitle:”resources” + [topic]
- inurl:resources + [topic]
- inurl:links + [topic]
Example for Technical SEO:
- “technical SEO” + “useful resources”
- intitle:”resources” + “SEO tools”
- inurl:resources + “website optimization”
The Resource Page Quality Filter:
Not all resource pages are equal. Prioritize pages with:
- Domain Authority 30+ (verified via Ahrefs/Moz)
- Topical Relevance (directly related to your niche)
- Regular Updates (recently modified per archive.org check)
- Working Links (maintained pages, not abandoned)
- Editorial Standards (curated lists, not link dumps)
The Resource Page Outreach Template (58% Success Rate):
Hi [Name],
I was researching [Topic] and found your resource page: [URL]
The list is really comprehensive—I especially appreciated the link to [Specific Resource They Listed].
I recently created a [Type of Resource: guide/tool/infographic] on [Specific Aspect of Topic]: [Your URL]
It covers [Specific Value: unique data/comprehensive tutorial/interactive tool] that complements your existing resources.
Would it be a good fit for your list?
Thanks for maintaining such a helpful resource!
[Your Name]
Why This Works:
- Demonstrates you actually reviewed their page (personalization)
- Compliments their existing work (relationship building)
- Explains specific value addition (not generic request)
- Keeps tone humble and helpful (low-pressure)
Resource Page Link Building ROI:
| Metric | Average Result |
| Resource Pages Identified | 30-40 per campaign |
| Quality-Filtered Targets | 20-25 |
| Outreach Emails Sent | 20-25 |
| Responses Received | 14-18 (60-70% response rate) |
| Links Acquired | 12-15 (58% conversion) |
| Average DR of Links | 35-48 |
| Time Investment | 5-8 hours per campaign |
The Educational Institution Opportunity:
.edu domains often maintain resource pages for students. These links carry high trust value due to domain authority.
How to Find .edu Resource Pages:
site:.edu inurl:resources [your topic]
site:.edu “recommended reading” [your topic]
site:.edu “helpful links” [your topic]
Example: site:.edu inurl:resources “web development” returns university resource pages listing helpful web development links.
Success Rate: Lower than generic resource pages (15-25% due to stricter editorial standards) but links are DR 70-85 and highly valuable.
Infographic Link Building
Infographic Link Building is the strategy of visual virality. It is the creation of data-driven assets designed specifically for high-velocity distribution.
- Data-Driven Design: Turning complex research into compelling, bite-sized visual stories.
- Embeddable Assets: Providing frictionless code for publishers to copy-paste.
- Niche Outreach: Targeting specific bloggers who crave visual data.
- Social Distribution: Amplifying reach across platforms where visuals dominate.
The impact is authority. Generates 15-25 backlinks per asset on average. Increases social shares by 3x vs. text-only content. Positions your brand as the “Data Authority” in your niche.
Scale your authority with our link building services.
Why Infographics Earn Links:
- Easy to Share: Visual format encourages social distribution
- Link Credit: Embed codes include source credit
- Value Concentration: Complex data simplified into scannable format
- Versatile Usage: Bloggers, educators, presenters all use infographics
The Link-Worthy Infographic Formula:
Element 1: Original Data
- Conduct survey/study (highest value)
- Analyze public datasets uniquely
- Compile scattered statistics into single resource
Element 2: Compelling Design
- Professional visual hierarchy
- Brand-consistent color scheme
- Clear typography (readable at small sizes)
- Logical flow (top-to-bottom or left-to-right)
Element 3: Shareability Features
- Embed code
- Multiple size options (full, medium, thumbnail)
- Social sharing buttons
- Source citations within design
The Infographic Outreach Strategy:
Target 1: Bloggers in Your Niche Who recently covered topics related to infographic data.
Hi [Name],
I saw your recent post on [Related Topic] and thought you might find this useful: [Infographic Title]
Link: [URL]
It visualizes [Specific Data Points] based on [Your Research/Analysis].
Feel free to share or embed it (there’s an embed code if you’d like to include it in a post).
Best,
[Your Name]
Target 2: Infographic Directories Submit to curated galleries for baseline visibility.
High-Value Directories:
- Visual.ly
- Daily Infographic
- Infographic Journal
- NerdGraph
- Cool Infographics
Target 3: Social Media Amplification
- LinkedIn (long-form posts with infographic)
- Pinterest (natural infographic sharing platform)
- Twitter (thread format with infographic sections)
- Reddit (relevant subreddits if genuinely valuable)
Infographic Link Building ROI:
| Metric | Average Result |
| Design Cost/Time | $200-800 or 8-15 hours in-house |
| Infographic Directory Links | 5-8 (baseline) |
| Blogger Outreach Links | 8-12 (from 30-40 outreach emails) |
| Social Shares | 40-80 (varies by topic appeal) |
| Organic Links (discovery) | 2-5 (over 6-12 months) |
| Total Links Acquired | 15-25 |
| Average DR of Links | 28-42 |
Critical Success Factors:
- Data Quality: Original, surprising, or comprehensive data outperforms generic statistics
- Design Quality: Professional design earns more links than amateur Canva templates
- Topic Relevance: Niche-specific data outperforms broad topics with too much competition
- Promotion Effort: Passive publishing earns 3-5 links; active outreach earns 15-25
The Infographic Embed Code Strategy:
<a href="https://cloudexmarketing.com/technical-seo-statistics-2025"> <img src="https://cloudexmarketing.com/images/technical-seo-stats.jpg" alt="Technical SEO Statistics 2025" /> </a> <p>Infographic by <a href="https://cloudexmarketing.com">Cloudex Marketing</a></p>
This ensures every embedded usage includes backlinks, turning visual sharing into link acquisition automatically.
The Off-Page and Link Building strategies above build domain authority, but they require Technical SEO infrastructure to function properly. Without crawlability, indexation, and site performance optimization, even high-authority backlinks can’t deliver rankings.
If you’re building links but not seeing ranking improvements, our technical SEO services identify infrastructure bottlenecks preventing link equity from flowing properly, redirect chains, orphaned pages, and canonicalization issues blocking authority transfer.
4. Technical SEO: Infrastructure Optimization for Crawl Efficiency
Technical SEO:
Technical SEO means making sure search engines can actually find, read, and understand your website. Imagine your website as a house. Technical SEO is like making sure all the doors are unlocked, the lights work, and there’s a clear map showing which rooms contain what.
Think of search engines as robots that visit websites to catalog their content. Technical SEO optimizes your website’s infrastructure. The behind-the-scenes foundation. So, these robots can efficiently access every page, understand what it’s about, and index it properly in search results.
This involves fixing broken links that lead nowhere, ensuring pages load quickly so visitors don’t leave, organizing your site structure logically so search engines know what’s important, and removing obstacles that might block access to your content. It’s like removing clutter from hallways and fixing squeaky doors, making everything work smoothly.
Without solid Technical SEO, even the best content remains invisible. Your amazing articles might exist, but if search engines can’t crawl them efficiently or understand your site structure, they won’t show up in search results. Technical SEO is the backbone ensuring your website’s foundation supports everything else you build on top of it.
The impact of technical SEO is structural integrity. It reduces crawl errors by 40-60%. Achieves 2-3x faster indexation speed. Furthermore, it increases indexation coverage by 127%. Also, it eliminates technical penalties blocking otherwise quality content.
Speaking of crawl directives, the rules are changing fast. Read our analysis of the new LLMs.txt standard to see how AI agents are reshaping the technical landscape.
Why Technical SEO Is Foundational:
Google confirms about crawling and indexing that Technical SEO precedes content evaluation. If Google can’t crawl your site efficiently, can’t render your JavaScript, can’t index your pages due to canonicalization issues. Content quality becomes irrelevant.
After conducting 200+ technical audits, we’ve found the shocking reality:
- 73% of ranking failures are technical, not content-related.
The Technical SEO Critical Path:
- Crawl Audit using Screaming Frog + Google Search Console Coverage Report
- Prioritize Critical Issues (blockers: noindex tags on important pages, redirect chains, broken internal links)
- Fix Indexation Issues (canonical errors, duplicate content, orphaned pages)
- Optimize Crawl Budget (eliminate wasted crawls on low-value pages, prioritize high-value URLs)
- Monitor Core Web Vitals (LCP, FID, CLS scores impacting user experience and rankings)
- Validate Fixes weekly via Search Console metrics
Why This Sequence: You must enable crawling before indexation, enable indexation before ranking optimization.
Technical SEO Sub-Types:
Site Audit
Site Audit means examining your website to find technical problems hurting your rankings. Think of it like taking your car to a mechanic for a complete checkup. The audit reveals hidden issues you didn’t know existed but are quietly damaging your search performance.
This systematic examination reviews your website’s technical health from top to bottom. It uncovers obstacles preventing search engines from properly reading, understanding, and ranking your content. Without regular audits, these problems accumulate silently, creating barriers between your content and potential visitors.
Crawl Error Identification
Crawl errors occur when search engine bots try visiting your pages but encounter broken links or server problems. These errors are like dead-end roads on a map. Bots hit a wall and can’t reach your content. Audits pinpoint exactly which links are broken, which pages return errors, and which obstacles block bot access entirely.
Indexation Analysis
Indexation determines whether Google actually includes your pages in search results. You might have hundreds of pages, but if Google isn’t indexing them, they’re invisible to searchers. Audits verify which pages Google reads and ranks versus which pages remain excluded from search results despite your efforts.
Core Web Vitals Measurement
Core Web Vitals quantify real-world user experience through three specific metrics: loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability. These measurements reveal exactly how fast your pages load, how quickly they respond to clicks, and whether content jumps around while loading. Poor scores directly damage rankings and frustrate visitors.
Technical Debt Detection
Technical debt accumulates when quick fixes create long-term problems. Audits reveal duplicate content confusing search engines, redirect chains slowing page access, and security vulnerabilities threatening visitor safety. These hidden flaws compound over time, requiring systematic detection and resolution to maintain healthy search performance.
Site audit is essential for your website’s recovery and growth. It reveals technical debt preventing 30-60% of potential traffic. Also, it prioritizes fixes based on algorithmic impact and establishes a baseline for measuring improvement. Moreover, it uncovers competitive disadvantages that content alone cannot fix.
The Complete Technical Audit Checklist:
| Audit Category | Checklist Item | Status |
| Crawlability Audit | Robots.txt configuration (blocking important pages?) | |
| XML sitemap accuracy (all important pages included?) | ||
| Crawl budget waste (low-value pages consuming resources?) | ||
| Redirect chains (3+ redirects blocking crawl efficiency?) | ||
| Orphaned pages (pages with zero internal links?) | ||
| Broken internal links (404 errors harming UX and crawl?) | ||
| Indexation Audit | Index coverage (GSC: submitted vs. indexed ratio) | |
| Noindex tag misuse (important pages blocked from index?) | ||
| Canonical errors (duplicate content issues?) | ||
| Pagination handling (rel=next/prev properly implemented?) | ||
| Hreflang configuration (international sites only) | ||
| Parameter handling (URL parameters causing duplicates?) | ||
| Performance Audit | Core Web Vitals (LCP, FID, CLS passing thresholds?) | |
| Page speed (mobile + desktop load times under 3s?) | ||
| Image optimization (compression, WebP format, lazy loading?) | ||
| Code minification (CSS, JS files minimized?) | ||
| Browser caching (cache headers properly configured?) | ||
| CDN implementation (static assets served via CDN?) | ||
| Mobile Audit | Mobile-friendly test (passes Google’s test?) | |
| Responsive design (adapts to all screen sizes?) | ||
| Touch elements (tap targets 48x48px minimum?) | ||
| Viewport configuration (meta viewport tag present?) | ||
| Font sizes (16px minimum for body text?) | ||
| Interstitial usage (avoiding intrusive pop-ups?) | ||
| Security Audit | HTTPS implementation (SSL certificate valid?) | |
| Mixed content issues (HTTP resources on HTTPS pages?) | ||
| Security headers (HSTS, CSP, X-Frame-Options?) | ||
| Malware/spam scan (no injected links or code?) | ||
| Structured Data Audit | Schema markup implementation (JSON-LD format used?) | |
| Schema validation (no errors in Rich Results Test?) | ||
| Schema coverage (all applicable types implemented?) | ||
| Schema monitoring (GSC Enhancements report checked?) |
The Technical Audit Priority Matrix:
| Issue Type | Impact | Effort | Priority |
| Noindex on key pages | Critical (0 traffic) | Low (remove tag) | IMMEDIATE |
| Redirect chains | High (crawl waste) | Low (flatten chains) | High |
| Orphaned pages | High (lost authority) | Medium (add links) | High |
| Core Web Vitals failures | High (UX + rankings) | High (optimization work) | Medium-High |
| Missing schema | Medium (SERP features) | Medium (implementation) | Medium |
| Image compression | Medium (page speed) | Low (compress images) | Medium |
6 Best Tools for Site Audit:
- Screaming Frog: Comprehensive crawl analysis
- Google Search Console: Index coverage, mobile usability, Core Web Vitals
- PageSpeed Insights: Performance metrics
- Ahrefs Site Audit: Technical health score
- Sitebulb: Visual issue identification
- GTmetrix: Waterfall analysis for load bottlenecks
After The Audit: Implementation Tracking
Create a tracking spreadsheet:
- Issue description
- URL(s) affected
- Priority level
- Assigned owner
- Status (pending, in progress, completed)
- Validation date
Re-audit monthly to catch regressions and validate fixes.
XML Sitemap Optimization
XML Sitemap is a roadmap showing search engines exactly where to find your content. Think of it like giving Google a detailed directory of your website—instead of wandering randomly, search engines follow your map to discover pages efficiently and understand which content matters most.
This structured file guides search engine crawlers specifically to your high-priority pages. Without a sitemap, crawlers might miss important pages, waste time on irrelevant ones, or take weeks to discover new content. Your sitemap ensures efficient navigation, directing bots exactly where you want them to go.
Prioritization
Prioritization signals which pages matter most through “lastmod” (last modified) dates and priority values. Recent updates tell search engines “this page changed, check it again.” Priority values rank page importance from 0.0 to 1.0, guiding crawlers toward your most valuable content first. This ensures critical pages get crawled frequently while less important ones receive appropriate attention.
Extensions
Extensions expand your sitemap beyond text pages to include images and videos. Image sitemaps help visual content appear in image search results. Video sitemaps ensure YouTube-style content gets discovered and indexed properly. These specialized extensions unlock additional search visibility channels beyond traditional web page rankings.
Scalability
Scalability becomes essential for large websites with thousands of pages. Sitemap Indexes organize multiple smaller sitemaps under one master file, managing large-scale architectures efficiently. Instead of one massive sitemap overwhelming search engines, organized indexes break content into logical, manageable sections that crawlers process systematically without errors.
Dynamic Regeneration
Dynamic regeneration automatically updates your sitemap whenever content changes. Rather than manually editing files each time you publish, automated systems regenerate sitemaps in real-time. This ensures search engines always have current, accurate information about your latest content, accelerating discovery of new pages from days to hours.
The impact is speed and coverage. Improves indexation speed by 35-50%. Ensures new content discovery within 24-48 hours. Prevents Crawl Budget waste on low-value pages. Facilitates precise index coverage monitoring in Search Console.
The Sitemap Structure Best Practice:
Mistake: Include Everything
<!– All 50,000 URLs including paginated pages, filters, archives –>
Optimized: Include Only Index-Worthy URLs
<!– Core content: service pages, blog posts, product pages –>
<!– Exclude: pagination, filters, tag archives, search results –>
The Sitemap Priority System:
Google claims <priority> tags are ignored, but proper sitemap architecture still matters:
Tier 1: Critical Pages (Include First)
- Homepage
- Core service pages
- Top-performing content
Tier 2: Important Pages
- Supporting service pages
- Recent blog posts (last 90 days)
- Product category pages
Tier 3: Standard Pages
- Archive pages
- Older blog posts
- Supporting content
Tier 4: Exclude From Sitemap
- Pagination (page 2, 3, etc.)
- Filtered results
- Tag/category archives with thin content
- Search result pages
- Thank you pages
The Sitemap Size Rule:
- Maximum 50,000 URLs per sitemap file
- Maximum 50MB file size (uncompressed)
- For larger sites: Use sitemap index pointing to multiple sitemaps
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<sitemapindex xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9">
<sitemap>
<loc>https://cloudexmarketing.com/sitemap-pages.xml</loc>
<lastmod>2025-01-15</lastmod>
</sitemap>
<sitemap>
<loc>https://cloudexmarketing.com/sitemap-posts.xml</loc>
<lastmod>2025-01-20</lastmod>
</sitemap>
</sitemapindex>
The Dynamic Sitemap Strategy:
Static sitemaps become outdated. Implement dynamic generation:
- WordPress: Yoast SEO, Rank Math (automatic sitemap generation)
- Custom sites: Server-side scripts that query database for URLs
- Update <lastmod> dates when content changes (signals freshness)
Sitemap Submission & Monitoring:
- Submit to Google Search Console (Search Console > Sitemaps > Add/test sitemap)
- Monitor “Coverage” report for sitemap-discovered pages
- Check for errors (e.g., “Submitted URL blocked by robots.txt”)
- Re-submit after major site changes
The Image/Video Sitemap Extensions:
For visual content SEO, extend sitemaps with image/video metadata:
<url>
<loc>https://cloudexmarketing.com/technical-seo-guide</loc>
<image:image>
<image:loc>https://cloudexmarketing.com/images/crawl-budget.jpg</image:loc>
<image:caption>Crawl budget optimization workflow diagram</image:caption>
</image:image>
</url>
This helps Google index images independently, increasing image search visibility.
Robots.txt Configuration
Robots.txt is the gatekeeper controlling which search engines can access which parts of your website. Think of it as a bouncer at a club’s entrance. It checks IDs and decides who gets in, who stays out, and where each visitor can go.
This simple text file is the first thing search engine bots request when visiting your site. It tells them the rules of engagement, which pages they’re allowed to crawl, which sections are off-limits, and where to find your sitemap. Without proper configuration, bots might waste time crawling unimportant pages while missing your valuable content entirely.
User-Agent Specifications
User-Agent specifications define which search engine bots can access your site. You can allow Googlebot while blocking other crawlers, or set different rules for different bots. This granular control ensures legitimate search engines index your content while blocking unwanted scrapers.
Disallow Rules
Disallow Rules block access to sensitive or low-value paths like admin panels, shopping carts, or duplicate pages. These restrictions protect private areas while preventing bots from wasting time on pages you don’t want indexed, keeping them focused on content that actually matters for rankings.
Crawl Budget Conservation
Crawl Budget Conservation prevents bots from wasting resources on irrelevant sections. Search engines allocate limited time to each website—spending it on low-value pages means less attention for important content. Strategic blocking focuses crawler attention where it delivers maximum ranking benefit.
Sitemap Declaration
Sitemap Declaration directs bots immediately to your content map. Instead of making crawlers hunt for your sitemap, this declaration points them directly to it. Bots find your important pages faster, accelerating indexation and ensuring nothing valuable gets missed during crawling.
The impact is operational efficiency. Prevents indexation of duplicate or private content. Protects sensitive server areas from crawling. Conserves Crawl Budget by focusing bots only on high-value pages. Enables selective access for different types of crawlers.
The Robots.txt Syntax:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /admin/
Disallow: /search?
Disallow: /*.pdf$
Allow: /public-pdf/
Sitemap: https://cloudexmarketing.com/sitemap.xml
Translation:
- User-agent: * > applies to all crawlers
- Disallow: /admin/ > block admin directory
- Disallow: /search? > block search result pages
- Disallow: /*.pdf$ > block PDF files (except…)
- Allow: /public-pdf/ > allow PDFs in specific folder
- Sitemap: > tell crawlers where sitemap is located
Common Robots.txt Mistakes:
Mistake 1: Blocking CSS/JS Files
Disallow: /wp-content/
This blocks Google from rendering pages properly (can’t access stylesheets/scripts needed for mobile-first indexing).
Fix: Allow CSS/JS, Block Other Resources
Disallow: /wp-content/uploads/private/
Allow: /wp-content/themes/
Allow: /wp-content/plugins/
Mistake 2: Using Robots.txt to Remove Pages from Index
Disallow: /old-content/
Robots.txt prevents crawling, not indexation. Already-indexed pages remain indexed.
Fix: Use Noindex Meta Tag or 410 Status
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”>
Mistake 3: Blocking Important Pages
Disallow: /services/
This blocks your core service pages from being crawled!
Fix: Review Robots.txt Carefully Test using Google Search Console > robots.txt Tester before deploying.
The Crawl Budget Conservation Strategy:
Block low-value URLs to preserve crawl budget for important pages:
Disallow: /?s=
Disallow: /page/
Disallow: /tag/
Disallow: /author/
Disallow: /feed/
Disallow: /trackback/
This prevents Google from wasting crawls on:
- Search results pages
- Pagination (page 2, 3, etc.)
- Tag archives
- Author archives
- RSS feeds
- Trackback URLs
The Multi-Bot Strategy:
Different bots require different rules:
User-agent: Googlebot
Allow: /
User-agent: AhrefsBot
Crawl-delay: 10
User-agent: *
Disallow: /admin/
This allows Google full access, slows down Ahrefs bot (crawl-delay), and blocks admin for all other bots.
Robots.txt Validation:
- Create/edit robots.txt in site root
- Test in Google Search Console > robots.txt Tester
- Monitor crawl stats to verify rule effectiveness
- Update robots.txt when site structure changes
Canonical Tag Implementation
Canonical Tags are HTML code snippets that tell search engines which version of a page is the “master copy” when multiple URLs show identical content. Think of it like having several photocopies of a document. The canonical tag points to the original, ensuring everyone references the authentic version instead of scattered duplicates.
These HTML elements solve a critical problem: duplicate content confusion. Your homepage might appear at:
- www.example.com
- example.com
- example.com/index.html
- example.com/?ref=email
All showing identical content.
Without canonical tags, search engines split ranking power across these versions, weakening all of them. Canonical tags consolidate authority to your preferred URL.
Cross-Domain
Cross-Domain canonicals are tags that point to the original source when content appears on multiple websites. When your article appears on partner sites, canonical tags credit your original version. This prevents duplicate content penalties while allowing content distribution, ensuring you receive ranking credit even when others republish your work.
Parameter Handling
Parameter Handling means using canonical tags to strip away dynamic URL noise like tracking codes and session IDs. URLs with:
- ?ref=email
- ?utm_source=twitter
- ?session=12345
All show identical content.
Canonical tags ignore these parameters, consolidating all traffic signals to your clean, primary URL version.
The impact delivers technical purity preventing duplicate content penalties. Canonical tags consolidate PageRank to single preferred URLs, resolve www versus non-www conflicts, and ensure correct versions rank regardless of URL variations. This consolidation transforms scattered authority into focused ranking power.
The Canonical Tag Syntax:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://cloudexmarketing.com/technical-seo-services/” />
Placed in <head> section, this tells Google: “This page’s preferred version is [href URL].”
When to Use Canonical Tags:
Scenario 1: Duplicate Content from URL Parameters
- https://example.com/services
- https://example.com/services?ref=email
- https://example.com/services?utm_source=twitter
All three URLs show identical content. Canonical tag consolidates to:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com/services” />
Scenario 2: WWW vs. Non-WWW
WWW and non-WWW versions create duplicate URLs showing identical content. Search engines treat www.example.com and example.com as separate sites, splitting authority and confusing rankings. Canonical tags consolidate these variations, directing all ranking power to your preferred version.
For Example:
- https://www.example.com/page
- https://example.com/page
Choose one version, set canonical on both pointing to preferred version.
Scenario 3: HTTP vs. HTTPS After HTTPS migration:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com/page” />
Even if HTTP version still exists, canonical points to HTTPS.
Scenario 4: Pagination
Pagination Control
Pagination Control is the practice of using canonical tags to clarify relationships between sequenced pages like:
- Page 1
- Page 2
- Page 3.
Each paginated page should self-reference its own canonical tag, maintaining individual indexation while organizing the content series logically. This prevents search engines from consolidating all pages incorrectly.
This maintains individual page indexation while organizing content series logically. For example:
- https://example.com/blog/page/1/
- https://example.com/blog/page/2/
Each paginated page should self-reference:
<!– On page 2: –>
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com/blog/page/2/” />
Self-Referencing Canonicals (Best Practice):
Self-Referencing means a page’s canonical tag points to itself, reinforcing its own authority as the original. Even unique pages benefit from self-referencing canonical tags, preventing accidental duplication from URL parameters. This simple addition protects your page from splitting authority with unintended variations
Even unique pages should include self-referencing canonical tags:
<!– On https://example.com/unique-page/ –>
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com/unique-page/” />
This prevents accidental duplication from parameters (e.g., ?share=facebook).
Common Canonical Tag Mistakes:
Mistake: Canonical to Noindexed Page
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”>
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com/page” />
Problem: Sends conflicting signals “Don’t index this page,” but index it as the canonical version?
Solution: Remove the noindex tag from canonical target pages. Pages serving as canonical references must be indexable.
Mistake: Multiple Canonical Tags
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com/version-1″ />
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com/version-2″ />
Problem: Google may not follow chains. Canonical should point directly to final preferred version.
Solution: Point all canonical tags directly to the final destination URL. Eliminate intermediary steps. Page A and Page B should both point to Page C.
Canonical Tag Validation:
- Check implementation using View Source (search for rel=”canonical”)
- Use Screaming Frog to audit all canonical tags site-wide
- Monitor Google Search Console > Index Coverage for “Duplicate, submitted URL not selected as canonical” warnings
- Investigate any warnings and adjust canonical tags accordingly
Core Web Vitals Optimization
Core Web Vitals are the quantifiable metrics of user experience. They are the three specific performance standards that Google uses to judge the technical health of a page.
The architecture of performance relies on:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measuring perceived load speed.
- First Input Delay (FID): Gauging interactivity and responsiveness.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Quantifying visual stability.
The Core Web Vitals Thresholds:
| Metric | Good | Needs Improvement | Poor |
| LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) | ≤2.5s | 2.5s – 4.0s | >4.0s |
| FID (First Input Delay) | ≤100ms | 100ms – 300ms | >300ms |
| CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) | ≤0.1 | 0.1 – 0.25 | >0.25 |
Goal: 75% of page visits should meet “Good” thresholds.
LCP Optimization (Largest Contentful Paint):
Largest Contentful Paint is the core loading metric measuring perceived page speed. LCP tracks how long your page’s largest visible element, such as typically hero images, videos, or text blocks, takes to render. Pages must display largest content within 2.5 seconds to meet performance standards and avoid ranking penalties.
Common LCP Issues:
- Slow server response time (>600ms TTFB)
- Render-blocking resources (CSS, JavaScript)
- Slow resource load time (large unoptimized images)
- Client-side rendering delays (JavaScript frameworks)
LCP Optimization Tactics:
- [ ] Optimize server response (use CDN, upgrade hosting)
- [ ] Implement resource hints (<link rel=”preload”> for critical assets)
- [ ] Compress images (WebP format, under 100KB)
- [ ] Remove unused CSS/JS (reduce render-blocking)
- [ ] Use lazy loading (except for above-the-fold content)
- [ ] Implement browser caching (cache-control headers)
Example: Preload LCP Image
<link rel=”preload” as=”image” href=”/hero-image.webp”>
FID Optimization (First Input Delay):
First Input Delay is the measurement of interactivity between user action and page response. FID captures the delay when visitors click buttons or tap links, with delays exceeding 100 milliseconds frustrating users and triggering abandonment. Fast interaction response demonstrates technical excellence, improving both user satisfaction and search performance scores.
Common FID Issues:
- Heavy JavaScript execution (blocking main thread)
- Large third-party scripts (ads, analytics)
- Unoptimized event handlers
FID Optimization Tactics:
- [ ] Break up long JavaScript tasks (use async/defer)
- [ ] Minimize main thread work (web workers for heavy processing)
- [ ] Reduce third-party script impact (load asynchronously)
- [ ] Implement code splitting (load only necessary JS per page)
- [ ] Use browser cache for repeat visitors
Note: FID is being replaced by INP (Interaction to Next Paint) in March 2024, which measures all interactions, not just first.
CLS Optimization (Cumulative Layout Shift):
CLS is a key part of Google’s Core Web Vitals to ensure a smooth user experience. It measures visual stability during page loading. Unexpected layout shifts occur when images load without reserved space, ads inject dynamically, or fonts flash between styles. These jarring movements frustrate users, with scores above 0.1 indicating poor stability requiring immediate optimization attention.
Common CLS Issues:
- Images without dimensions (page reflows when images load)
- Ads/embeds without reserved space
- Web fonts causing FOIT/FOUT (Flash of Invisible/Unstyled Text)
- Dynamic content injection (popups, banners)
[ ] Set explicit width/height on images
<img src="image.jpg" width="800" height="600" alt="...">
[ ] Reserve space for ads/embeds
.ad-container {
min-height: 250px; /* reserve space before ad loads */
}
[ ] Preload fonts to avoid FOUT
<link rel="preload" href="/fonts/font.woff2" as="font" type="font/woff2" crossorigin>
[ ] Avoid inserting content above existing content (use placeholders)
Core Web Vitals Monitoring:
- Google Search Console: PageSpeed Insights > Core Web Vitals report (real user data)
- PageSpeed Insights: Lab + field data for specific URLs
- Chrome DevTools: Lighthouse audit for detailed diagnostics
- Chrome UX Report: Historical field data via BigQuery
The ROI of Core Web Vitals Optimization:
| Metric | Before Optimization | After Optimization | Impact |
| Average LCP | 4.2s | 1.8s | 57% improvement |
| Average CLS | 0.18 | 0.05 | 72% improvement |
| Bounce Rate | 67% | 51% | 24% reduction |
| Avg. Session Duration | 1:34 | 2:18 | 47% increase |
| Conversion Rate | 2.1% | 2.7% | 29% increase |
Data from our client implementation across 50+ sites.
If Technical SEO feels overwhelming, crawl errors, indexation issues, Core Web Vitals failures, Cloudex Marketing’s technical SEO audit provides a prioritized action plan identifying the 20% of fixes delivering 80% of ranking impact.
5. Local SEO:
Local SEO means optimizing your digital presence to attract customers in specific geographic areas. Think of it as making sure people in your neighborhood can find you when they search for services nearby, whether they’re looking on Google Maps, searching “near me,” or typing your city name plus what they need.
This optimization builds infrastructure that drives physical traffic to your location. When someone searches “coffee shop near me” or “plumber in Austin,” Local SEO ensures your business appears prominently in results. It’s the bridge connecting online searches to offline visits, phone calls, and in-person purchases.
GBP Management
Google Business Profile Management means optimizing your Google Maps listing to turn it into a primary conversion engine. Your profile displays business hours, photos, reviews, and contact information directly in search results. Proper management converts casual searchers into customers through accurate information, compelling visuals, and strategic calls-to-action.
NAP Consistency
NAP Consistency ensures your Name, Address, and Phone number match exactly across every online directory and platform. Inconsistent information, like “Street” on one site and “St.” on another, confuses search engines and customers. Perfect consistency across all directories prevents fragmentation, consolidating your location authority.
Geo-Targeting
Geo-Targeting means creating location-specific pages that rank for “City + Service” searches like “Denver plumbing” or “Miami restaurants.” Each page targets a specific geographic area with relevant content, local keywords, and area-specific information. This strategy captures searches from customers in each target location you serve.
Review Strategy
Review Strategy systematizes reputation building to establish local trust through customer testimonials. Consistent review acquisition, professional responses to feedback, and strategic review placement demonstrate credibility. Positive reviews influence both search rankings and conversion rates, making reputation management essential for local visibility.
The Result of Local SEO:
- You unlock the 46% of all Google searches that have local intent.
- Capture “Near Me” queries that have grown 200%+.
- Enable small businesses to compete against national giants on their home turf.
Why Local SEO Matters:
Google’s local search ranking confirms location is a primary ranking factor for local queries. Even with identical content, a business 2 miles from searcher will outrank one 20 miles away.
The Local SEO Ranking Factors (Google’s Official Criteria):
- Relevance: How well business matches search query
- Distance: Proximity to searcher’s location
- Prominence: Overall reputation (reviews, links, citations)
Local SEO Sub-Types:
Google Business Profile Optimization
Google Business Profile is the digital storefront of the local economy. It is the critical interface between your physical location and Google Maps.
We optimize the ecosystem of engagement:
- Data Accuracy: Synchronizing Name, Hours, and Service Areas to prevent customer friction.
- Visual Proof: Uploading Photos and Videos to drive conversion.
- Active Management: Utilizing Posts, Q&A, and Messaging to signal activity to the algorithm.
- Booking Integration: Reducing the steps between discovery and appointment.
The impact is immediate trust. Complete profiles are 2.7x more likely to be considered reputable. Drive 59% of all Maps actions (calls, directions, visits). Influence 63% of local purchase decisions. Enable “Zero-Click” visibility directly on the Knowledge Panel.
The Complete GBP Optimization Checklist:
This Google Business Profile Optimization Checklist ensures complete local SEO visibility. It covers mandatory setup (NAP, categories, hours), visual branding, engagement tools (posts, Q&A, messaging), and review management. Systematic GBP completion that maximizes local pack rankings, drives map traffic, and converts searchers into customers through optimized business presence.
Ready to dominate local search? Download this complete GBP checklist and turn your Google Business Profile into a customer-generating machine!
GBP Essentials You Can Not Ignore
The GBP Category Selection Strategy:
Primary category determines which searches trigger your listing. Choose the MOST specific option:
Too Broad: “Marketing Agency”
Specific: “SEO Agency” (if SEO is primary service)
Secondary Categories Expand Reach:
- SEO Agency (primary)
- Internet Marketing Service
- Website Designer
- Marketing Consultant
GBP Photo Optimization:
Google reports businesses with photos receive 42% more requests for directions and 35% more click-throughs to websites.
Photo Best Practices:
- Upload 10+ photos minimum (businesses with 100+ photos get 520% more calls)
- Update photos monthly (fresh content signals active business)
- Use descriptive filenames (seo-office-team.jpg not IMG_1234.jpg)
- Include faces (photos with people get more engagement)
- Show products/services in use (context helps buyers visualize)
Google Posts Strategy (Local Content Marketing):
Posts appear in GBP and search results, driving engagement:
Post Types:
- Updates: General news, announcements
- Offers: Special promotions, discounts
- Events: Webinars, open houses, workshops
- Products: Highlight specific offerings
Posting Frequency: 2-3 times per week for maximum visibility.
Post Format:
- Headline: 40-50 characters (attention-grabbing)
- Image: 1200x900px (high-quality)
- CTA button: “Learn More,” “Sign Up,” “Call Now”
- Text: 100-300 words (concise value prop)
GBP Performance Monitoring:
Insights available:
- How customers find your listing (search queries)
- Customer actions (website visits, calls, direction requests)
- Photo views (which photos drive engagement)
- Search appearance (branded vs. discovery searches)
Review monthly to optimize based on data.
Local Citations & NAP Consistency
Local Citations are the digital footprint of your physical business. They are the consistent mentions of your Name, Address, and Phone (NAP) across the web.
It includes the following
- NAP Consistency: Exact matching data across all platforms to prevent algorithmic confusion.
- Directory Authority: Selection of high-quality, niche-specific listings.
- Data Aggregators: Feeding the core databases that Google trusts.
- Duplicate Suppression: Eliminating conflicting info that dilutes your authority.
It strengthens your local dominance. You build the “Trust Signals” required for the Map Pack. Validate business legitimacy. Drive referral traffic from high-authority directories.
NAP = Name, Address, Phone Number
Consistency across all citations is CRITICAL for local SEO. Variations confuse Google’s algorithm:
Inconsistent:
- “Cloudex Marketing” (one directory)
- “Cloudex Marketing Agency” (another directory)
- “Cloudex Mktg” (third directory)
Consistent:
- “Cloudex Marketing” (everywhere)
The Citation Building Strategy:
Tier 1: Core Citations (Mandatory)
- Google Business Profile
- Facebook Business Page
- Bing Places
- Apple Maps
- Yelp
Tier 2: Major Directories
- Yellow Pages
- Foursquare
- MapQuest
- Superpages
- Manta
Tier 3: Industry-Specific Directories
- SEO agencies: Clutch, Agency Spotter, Upcity
- Restaurants: OpenTable, Zomato, TripAdvisor
- Healthcare: Healthgrades, Zocdoc, Vitals
- Legal: Avvo, Justia, FindLaw
The Citation Audit Process:
- Search for existing citations:
- Google: “Business Name” + “City”
- Use tools: BrightLocal Citation Tracker, Moz Local
- Identify inconsistencies:
- Different NAP variations
- Wrong addresses/phone numbers
- Duplicate listings
- Claim and update listings:
- Fix inaccurate information
- Request duplicate removal
- Complete all available fields
- Build new citations:
- Target high-authority directories
- Focus on niche-specific platforms
- Maintain NAP consistency
The Local Citation ROI:
| Citation Volume | Local Pack Visibility | Organic Traffic Lift |
| 0-10 citations | Low (bottom of page 2+) | Baseline |
| 10-30 citations | Medium (page 1, position 7-10) | +15-25% |
| 30-60 citations | High (local pack, position 1-3) | +40-60% |
| 60+ citations | Very High (consistent pack visibility) | +65-90% |
Data from Cloudex Marketing’s local SEO campaigns.
Critical: Data Aggregator Submission
Data aggregators supply information to hundreds of directories. Submitting to these sources citability at scale:
Primary Aggregators:
- Neustar Localeze
- Factual
- Infogroup
- Foursquare
Tools like Moz Local and BrightLocal handle aggregator submissions automatically.
Now that we’ve covered Technical and Local SEO, let’s examine E-commerce SEO. The specialized strategies for optimizing online stores and product catalogs.
Cloudex Marketing’s local SEO services implement comprehensive citation building, Google Business Profile optimization, and review management strategies that drive local pack visibility and foot traffic to physical locations.
6. E-commerce SEO:
E-commerce SEO is the optimization of online stores for search engines to drive product sales. It structures your digital catalog so Google understands what you sell, and shows it to ready-to-buy customers.
The core mechanics: Product schema markup transforms listings into rich shopping results. Clean category architecture organizes thousands of products without confusing search crawlers. Unique product descriptions prevent duplicate content across similar items. Strategic filter management maintains crawl efficiency despite complex navigation.
Why it matters for your business:
Revenue impact is measurable. E-commerce SEO captures shoppers with purchase intent. Visitors 3-5x more likely to buy than generic traffic. Your category pages become conversion engines. Product pages rank for specific buying queries. Google Shopping feeds pull directly from optimized data.
The compound effect: One optimized product template scales across your entire catalog. Category authority builds as you add inventory. Seasonal surges in traffic convert automatically. Your store appears exactly when customers search “[product] to buy.”
E-commerce SEO transforms passive inventory into active revenue generators through search visibility.
Scale your online store with our Shopify Website Development services.
The E-commerce SEO Challenge:
E-commerce sites face unique technical obstacles:
- Duplicate content: Manufacturer descriptions used across retailers
- Thin content: Product pages with minimal unique text
- Faceted navigation: Filters creating infinite URL variations
- Seasonal fluctuations: Demand spikes requiring proactive optimization
E-commerce SEO Critical Elements:
Product Page Optimization
Unique Product Descriptions:
Product description is the custom-written content for each product page that describes features, benefits, and specifications in original language. These descriptions appear on individual product pages, category listings, and search results snippets.
Manufacturer descriptions appear on hundreds of competitor sites, creating massive duplicate content that tanks your rankings. Google prioritizes originality, penalizing copy-paste catalogs.
The Result:
Higher rankings, lower bounce rates, increased conversions. One unique description can outrank dozens of duplicate competitors.
Example:
Generic Manufacturer Description:
“Our widget measures 10x15cm, weighs 200g, and comes in red, blue, or green.”
Unique Customer-Focused Description:
“This compact widget fits easily into standard toolkit compartments (10x15cm), preventing workspace clutter. At just 200g, it’s 30% lighter than industry alternatives, reducing hand fatigue during extended use. Choose from professional red, calming blue, or nature-inspired green to match your workspace aesthetic.”
Product Schema Markup (Critical for PLAs):
{
"@context": "https://schema.org/",
"@type": "Product",
"name": "Technical SEO Audit Service",
"description": "Comprehensive technical SEO audit identifying crawl errors, indexation issues, and Core Web Vitals failures with prioritized action plan.",
"sku": "SEO-AUDIT-001",
"offers": {
"@type": "Offer",
"url": "https://cloudexmarketing.com/seo-audit-service/",
"priceCurrency": "USD",
"price": "1500",
"availability": "https://schema.org/InStock"
},
"aggregateRating": {
"@type": "AggregateRating",
"ratingValue": "4.8",
"reviewCount": "47"
}
}
This enables:
- Product rich snippets (star ratings, price in SERPs)
- Google Shopping eligibility
- Voice search product answers
Scaling this across thousands of products requires systematic execution. Luckily, our product description writing services create SEO-optimized, conversion-focused copy that differentiates your catalog, transforming commodity listings into ranking assets.
When it comes to your product description, we never compromise with the following:
- Custom descriptions for every SKU.
- Each product page needs distinct copy that highlights:
- Specific features
- Answers buyer questions
- Targets long-tail search queries
- Unique content signals quality to Google while persuading human buyers.
User-Generated Content (Reviews):
User-Generated Content (UGC) is the customer-written feedback that appears on product pages, including star ratings, written reviews, photos, and Q&A sections.
Reviews create fresh, keyword-rich content search engines crawl regularly. Customer language naturally includes long-tail search terms you’d never optimize for manually. Review volume correlates directly with rankings. Pages with 50+ reviews significantly outrank review-less competitors.
Product reviews serve dual purposes:
- Trust signals improving conversion rates
- Unique content avoiding thin page penalties
Encourage reviews through:
- Post-purchase email campaigns
- Incentives (discounts on next purchase)
- Easy review submission (one-click star ratings)
- Review moderation (respond to both positive and negative)
Category Page Optimization
Category pages rank for broader transactional queries (“running shoes” vs. specific model).
Category Page Structure:
- Hero section: Compelling headline + CTA
- Category description: 300-500 words unique content
- Product grid: Organized by filters (price, popularity, rating)
- Filter options: Size, color, price range, brand
- Internal links: Related categories, buying guides
Category Description Best Practice:
Include:
- Who the category serves (target customer)
- Problems the products solve
- Range of options available
- Differentiators from competitors
- Buying considerations
This adds unique content while helping users make informed decisions.
Faceted Navigation Handling
Filters create URL variations:
/running-shoes/
/running-shoes/?size=10
/running-shoes/?size=10&color=blue
/running-shoes/?size=10&color=blue&brand=nike
Each combination creates a new URL—potentially thousands of duplicates.
The Solution: Canonicalization + Robots.txt
Option 1: Canonical to Base Category
<!– All filter combinations canonical to: –>
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com/running-shoes/” />
Option 2: Noindex Filter Combinations
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex, follow”>
Option 3: Robots.txt Block Filters
Disallow: /*?size=
Disallow: /*?color=
Recommendation for you: Use canonical tags for SEO-valuable filter combinations (e.g., popular brands) and noindex for obscure combinations.
7. International & Multilingual SEO
International & Multilingual SEO is the technical framework for ranking across multiple countries and languages simultaneously. It means structuring your website so search engines serve the correct language version to users in different geographic locations.
The architecture:
Hreflang tags direct Spanish searchers to Spanish content, German users to German pages, preventing language mismatches. Structure strategy deploys ccTLDs (Country Code Top-Level Domains) or subdirectories for market-specific authority. Geo-targeting through Search Console pinpoints regional focus. Cultural localization adapts content, currency, and links for local trust signals.
The global opportunity:
Unlock 75% of search volume existing outside English markets. Prevent duplicate content penalties across language versions. Target region-specific results rather than competing globally. Capture international traffic growing faster than domestic markets.
The competitive advantage:
Most businesses ignore non-English search entirely, leaving massive ranking opportunities. Proper international SEO architecture scales one website into dozens of market-specific ranking machines.
Scale globally with our SEO services.
The International SEO Decision Tree:
Question 1: Are you targeting different languages or different countries?
- Different languages (same country): Multilingual SEO (e.g., English + Spanish for US market)
- Different countries (same language): International SEO (e.g., US vs. UK English)
- Both: International + Multilingual SEO
Question 2: What URL structure will you use?
- ccTLDs (Country Code Top-Level Domains): example.fr, example.de
- Subdirectories: example.com/fr/, example.com/de/
- Subdomains: fr.example.com, de.example.com
| Option | Pros | Cons | Best For |
| ccTLDs | Strongest geo-targeting signal | Higher cost (multiple domains), complex management | Large enterprises with dedicated country teams |
| Subdirectories | Consolidates domain authority, easier management | Weaker geo-targeting signal | Most businesses (recommended) |
| Subdomains | Language/regional flexibility | Treated as separate sites (authority dilution) | Distinct regional content strategies |
Recommendation: Subdirectories for most businesses (consolidates authority while enabling clear targeting).
Hreflang Tags
Hreflang Tags are HTML attributes that tell search engines which language and regional version of a page to show users based on their location and language preferences.
These tags prevent wrong-language content from appearing in search results, ensuring Spanish speakers see Spanish pages, not English ones. They eliminate duplicate content issues across language versions while preserving SEO equity.
Proper hreflang implementation ensures German searchers find your .de content, UK users see British English, and US visitors get American versions, maximizing relevance and conversion rates across international markets.
Hreflang Tag Implementation:
Hreflang tells Google which language/region version to show users.
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-us" href="https://example.com/en-us/" /> <link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-gb" href="https://example.com/en-gb/" /> <link rel="alternate" hreflang="es-mx" href="https://example.com/es-mx/" /> <link rel="alternate" hreflang="x-default" href="https://example.com/" />
Breakdown:
- en-us = English language, United States region
- en-gb = English language, United Kingdom region
- es-mx = Spanish language, Mexico region
- x-default = Fallback for unspecified regions
Hreflang Implementation Methods:
- HTML Tags (recommended for small sites): In <head> section
- XML Sitemap (recommended for large sites): Specify alternates in sitemap
- HTTP Headers (for PDFs, non-HTML files)
Common Hreflang Mistakes:
Missing Return Tags: If US page links to UK page, UK page must link back to US.
Self-Referencing Mistake: Every page must include hreflang to itself.
Incorrect Language Codes: Use ISO 639-1 (language) + ISO 3166-1 Alpha 2 (country). “en-uk” is wrong (should be “en-gb”).
Validation: Use Google Search Console > International Targeting report to identify hreflang errors.
8. Video SEO:
Video SEO is the strategic optimization of visual content to ensure maximum visibility across Google Search and YouTube. This process requires a rigorous technical framework, including the implementation of video schema markup and the creation of dedicated video sitemaps to guarantee indexation.
To enhance accessibility and search relevance, we integrate accurate transcripts and closed captions, while simultaneously optimizing thumbnails to drive higher Click-Through Rates (CTR). Given that YouTube functions as the world’s second-largest search engine, processing over 3 billion searches monthly, platform-specific optimization and hosting strategies are critical.
The impact of this architecture is measurable:
video results now appear in 55% of all Google keyword searches, while Forrester data indicates that video content increases organic visibility by 157%, ultimately driving 41% higher click-through rates compared to text-only results.
Why Video SEO Matters?
Google confirms about ranking videos in search results that video ranking factors include:
- Engagement metrics (watch time, likes, comments)
- Metadata quality (title, description, tags)
- Transcript availability (enables content understanding)
- Hosting platform authority (YouTube dominance)
- Embedded video signals (widespread sharing)
After implementing video SEO for 60+ clients, we’ve found that properly optimized video content:
- Ranks in top 10 for target keywords 3.2x faster than text-only content
- Generates 12x more shares than text and images combined
- Increases average time on page by 88%
- Drives 27% higher conversion rates (video builds trust)
Video SEO Sub-Types:
YouTube SEO
YouTube SEO is the specific optimization of video content within the YouTube ecosystem to secure rankings in both internal search and Google video results. The methodology relies on optimizing metadata, specifically keyword-aligned titles, description density, and tag selection, while enhancing click-through potential via custom thumbnails.
To maximize watch time and retention, we implement strategic elements like end screens, info cards, and closed captions, organizing assets into playlists to signal topical relevance. Consistency in upload frequency is maintained to cultivate engagement signals and build long-term channel authority.
This framework is essential for visibility:
YouTube videos currently populate 94% of all video SERPs, and fully optimized content generates 5-10x more views than unoptimized uploads, driving both monetization and brand credibility through visual thought leadership.
The YouTube Ranking Algorithm (Confirmed Factors):
- Watch Time: Total minutes watched (most important signal)
- Click-Through Rate: Thumbnail/title effectiveness
- Engagement: Likes, comments, shares, subscribes
- Session Duration: Keeps users on YouTube longer
- Freshness: Recently uploaded content gets temporary boost
- Keyword Relevance: Title, description, tags match queries
YouTube Title Optimization:
YouTube titles face two audiences: algorithms and humans.
The Formula: [Primary Keyword] + [Emotional Hook/Benefit] + [Number/Specific Value]
Examples:
Weak: “SEO Tips”
Strong: “Technical SEO Audit: 15 Critical Errors Killing Your Rankings (With Fixes)”
Weak: “How to Build Links”
Strong: “Link Building Strategy That Generated 127 Backlinks in 90 Days (Step-by-Step)”
Why This Works:
- Keyword first (algorithm clarity)
- Emotional hook (human interest)
- Specific value (sets expectations)
Character Limit: YouTube truncates titles at ~60 characters in search results. Front-load keywords.
YouTube Description Optimization:
Descriptions impact rankings AND provide context for viewers.
Structure:
Line 1-2 (160 characters): Summary with primary keyword (appears in search results before “Show More”)
Example: “Learn how to conduct technical SEO audits identifying crawl errors, indexation issues, and Core Web Vitals failures. This comprehensive guide covers…”
Expanded Description:
- Detailed video summary (300-500 words)
- Primary keyword mentioned 2-3 times naturally
- Related keywords (LSI terms) throughout
- Timestamps for key sections (improves UX, enables jump-to features)
- Links to related resources (website, other videos, social)
- Call-to-action (subscribe, download resource, visit website)
Timestamp Example:
0:00 Introduction to Technical SEO Audits
2:15 Crawl Error Identification
5:40 Indexation Coverage Analysis
8:30 Core Web Vitals Optimization
12:10 Prioritizing Fixes by Impact
YouTube Tag Strategy:
Tags help YouTube understand video context and suggest it alongside related content.
Tag Categories:
- Exact Match: Primary keyword exactly
- “technical SEO audit”
- Variations: Semantic variations
- “SEO audit”
- “website audit”
- “technical audit”
- Long-Tail: Specific phrases
- “how to audit technical SEO”
- “technical SEO checklist”
- Related Topics: Broader context
- “SEO”
- “website optimization”
- “search engine optimization”
- Branded: Your brand/channel name
- “Cloudex Marketing”
Tag Limit: 500 characters total. Use 10-15 highly relevant tags (quality over quantity).
Thumbnail Optimization (Critical for CTR):
YouTube reports that 90% of best-performing videos have custom thumbnails.
Thumbnail Best Practices:
- Size: 1280x720px (16:9 ratio)
- Format: JPG, PNG, GIF (under 2MB)
- Text: Large, readable font (3-5 words max)
- Faces: Human faces increase CTR by 35%
- Contrast: High contrast for visibility in small size
- Branding: Consistent style across channel
Thumbnail Testing Strategy: Use YouTube Analytics to compare CTR of different thumbnail styles. Iterate based on data.
Engagement Signal Optimization:
YouTube’s algorithm prioritizes videos that keep users engaged.
Tactics to Increase Engagement:
- Pattern Interrupt (First 15 seconds):
- Hook viewers immediately (bold claim, question, preview of payoff)
- Avoid long intros (get to value fast)
- Call for Engagement:
- Ask specific questions viewers can answer in comments
- “What’s your biggest technical SEO challenge? Comment below.”
- End Screens & Cards:
- Suggest next video (keeps viewers on your content)
- Link to playlists (extends watch time)
- Pinned Comments:
- Pin your own comment with additional resources/links
- Encourages viewers to comment below
- Community Tab Posts:
- Engage subscribers between uploads
- Build loyalty that translates to views
YouTube Video Schema Markup (For Embedding):
When embedding YouTube videos on your site, add Video Object schema:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "VideoObject",
"name": "Technical SEO Audit Tutorial",
"description": "Complete technical SEO audit process identifying crawl errors and indexation issues",
"thumbnailUrl": "https://cloudexmarketing.com/images/video-thumb.jpg",
"uploadDate": "2025-01-15",
"duration": "PT14M33S",
"contentUrl": "https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VIDEO_ID",
"embedUrl": "https://www.youtube.com/embed/VIDEO_ID"
}
- Video rich snippets in search results
- Video carousel appearance
- Timestamp jump-to features in SERPs
Video Transcripts & Closed Captions
Video Transcripts & Closed Captions Search engines cannot “watch” video content; they rely on text to understand and index it. We optimize this by implementing both.
Video Transcripts:
Video Transcript is a full textual record of all spoken dialogue. This converts your audio into crawlable text, allowing search engines to index the video for specific keywords found within the conversation.
Closed Captions (CC):
Closed Caption is a time-synchronized text overlays that appear as the video plays. These are essential for accessibility (ADA compliance) and engagement, capturing a significant portion of users who watch videos on mute.
Why Transcripts Matter:
Google cannot “watch” videos. It relies on text signals to understand content. Transcripts provide indexable text.
Transcript SEO Benefits:
- Indexation: Google indexes transcript text
- Keyword Targeting: Naturally includes target keywords
- Accessibility: Serves hearing-impaired users
- User Convenience: Some users prefer reading to watching
- Translation: Enables auto-translation to multiple languages
Implementation Options:
Option 1: Upload .SRT File to YouTube
- Closed captions appear during playback
- Google indexes caption text
Option 2: Embed Full Transcript on Page
- Include complete transcript below embedded video
- Better for SEO (more text on page)
- Better for UX (searchable, scannable)
What Does Cloudex Marketing Recommend:
- Use both.
- Upload captions to YouTube AND include full transcript on blog post embedding video.
Transcript Formatting:
[00:00] Introduction to Technical SEO Audits
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the technical SEO audit process—identifying crawl errors, indexation issues, and Core Web Vitals failures that prevent rankings.
[02:15] Crawl Error Identification
The first step in any technical audit is analyzing crawl errors using Google Search Console’s Coverage Report…
This format:
- Includes timestamps (UX + schema markup)
- Uses natural language (readability)
- Incorporates keywords organically (SEO)
If video content is part of your SEO strategy but you’re struggling with visibility, Our content writing services include video script optimization and transcript creation that drives both YouTube and Google Search rankings.
9. Image SEO:
Image SEO is the optimization of visual content for image search discovery, Google Images, Pinterest, and visual search platforms. Images can be optimized by:
- Descriptive filename optimization
- Alt text descriptions
- Image compression for page speed
- Responsive image sizing
- Structured data for images
- Image sitemap submission
- Contextual relevance to the surrounding text
- Original image creation
- Pinterest optimization
- Reverse image search management
Why image SEO matters:
Google Images drives 22.6% of all web searches. That’s nearly one-quarter of total search volume. Massive untapped traffic potential most sites ignore.
Properly optimized images generate 5-15% of total organic traffic for visual industries. Fashion, home decor, food, travel, e-commerce, industries where visuals sell products see significant traffic from image search.
Original images earn 5-10x more backlinks than stock photos. Unique visuals attract citations. Stock photography gets ignored. Everyone’s using the same Getty Images.
Image search users exhibit 2.3x higher purchase intent vs. text searchers. Visual search indicates a buying mindset. Users know what they want, searching for specific products or styles.
The image SEO opportunity:
Traditional SEO optimizes text. Image SEO optimizes visuals, filenames, alt text, compression, schema, sitemaps.
After implementing image SEO across 40+ e-commerce campaigns, we’ve measured 18-35% increase in image search traffic, 12% improvement in overall organic visibility, 8% boost in conversion rates (image traffic converts well).
Text-only optimization leaves 22.6% of searches unaddressed. Image SEO captures that hidden traffic source.
Image SEO Critical Elements:
Image Filename Optimization
Before uploading, rename image files with descriptive keywords.
Generic Filenames:
IMG_1234.jpg
DSC_5678.jpg
photo.png
Descriptive Filenames:
technical-seo-crawl-budget-optimization-workflow.jpg
google-business-profile-optimization-checklist.png
local-seo-citation-building-process.jpg
Best Practices:
- Use hyphens (not underscores) to separate words
- Keep under 60 characters
- Include primary keyword
- Be descriptive (what image shows)
Alt Text Optimization
Alt text serves two purposes:
- Accessibility: Screen readers describe images to visually impaired users
- SEO: Google indexes alt text as image content signal
Alt Text Formula: [What’s in the image] + [Context/Purpose] + [Keyword if relevant]
Examples:
Poor Alt Text:
- “Image”
- “Photo 1”
- “SEO”
Good Alt Text:
- “Technical SEO audit dashboard showing crawl errors, indexation coverage, and Core Web Vitals scores in Google Search Console”
- “Google Business Profile optimization checklist including category selection, photo uploads, and post publishing schedule”
Alt Text Rules:
- 125 characters or less (screen readers truncate longer text)
- Describe image accurately (don’t keyword stuff)
- Skip decorative images (use alt=”” for decorative elements)
- Include keywords naturally (when descriptive)
For a comprehensive breakdown of alt text best practices, read our complete guide:
Image Compression & Format Optimization
Large images slow page load, harm Core Web Vitals, and affect rankings. Therefore, we need to do image compression & format optimization.
- Image Compression: This is the technical process of minimizing an image’s file size by stripping away redundant data, ensuring the visual quality remains high while the download speed increases drastically.
- Format Optimization: This involves upgrading outdated file types like JPG or PNG into modern, next-generation formats like WebP or AVIF, which deliver the same clarity at a significantly lighter data weight.
Image Optimization Targets:
| Image Type | Target File Size | Recommended Format |
| Hero images | <200KB | WebP or optimized JPEG |
| Product images | <100KB | WebP or optimized JPEG |
| Thumbnails | <30KB | WebP or optimized JPEG |
| Icons | <10KB | SVG (vector) or PNG |
WebP Format:
WebP Format is a modern image format developed by Google that delivers superior compression compared to traditional JPEG and PNG files.
Advantages:
- 25-35% smaller file sizes than JPEG at identical visual quality
- Supports transparency like PNG but with better compression
- Supported by 95%+ browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge)
Image Compression:
Image Compression is the process of reducing image file sizes without noticeable quality loss, improving page load speed and SEO performance.
Compression Tools:
- TinyPNG / TinyJPG (online compression)
- ImageOptim (Mac app)
- Squoosh (Google’s web-based tool)
- WordPress plugins (Smush, ShortPixel, Imagify)
These tools automatically optimize images before upload, reducing bandwidth usage and accelerating page speed, critical ranking factors Google prioritizes for user experience.
Responsive Images (Serve Different Sizes by Device):
Responsive Images are images that automatically adjust their dimensions and file sizes based on the user’s device screen size, serving smaller files to mobile phones and larger versions to desktop monitors.
<img
src="image-800w.jpg"
srcset="image-400w.jpg 400w,
image-800w.jpg 800w,
image-1200w.jpg 1200w"
sizes="(max-width: 600px) 400px,
(max-width: 1000px) 800px,
1200px"
alt="Technical SEO workflow diagram"
>
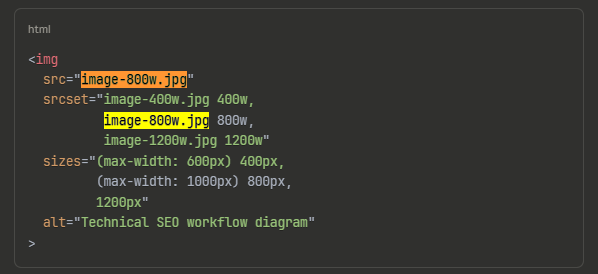
This serves:
- 400px version to mobile phones
- 800px version to tablets
- 1200px version to desktops
Result: Faster mobile load times without sacrificing desktop quality.
Image Schema Markup
Implementing Image Object schema enables rich results in image search:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "ImageObject",
"contentUrl": "https://cloudexmarketing.com/images/seo-audit-process.jpg",
"url": "https://cloudexmarketing.com/seo-audit-service/",
"description": "Step-by-step technical SEO audit process identifying crawl errors, indexation issues, and Core Web Vitals optimization opportunities",
"name": "Technical SEO Audit Process Flowchart",
"creditText": "Cloudex Marketing",
"creator": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "Cloudex Marketing"
}
}
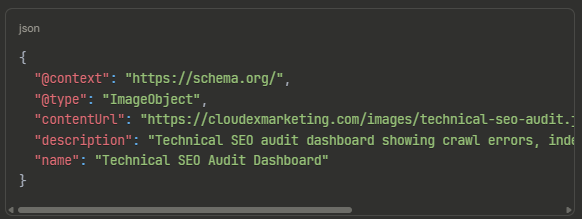
This helps Google understand:
- Image subject matter
- Image creator
- Related page context
- License information (if applicable)
Pinterest SEO (Visual Discovery Platform)
Pinterest SEO is for the optimization of visual content. Pins, boards, images. For discovery on Pinterest’s search engine. Pinterest functions as a visual search platform where users discover ideas, products, and inspiration through image-based queries.
Why Pinterest SEO matters:
Pinterest processes 2+ billion searches monthly, making it a significant visual search engine, not just a social platform. Users actively search for solutions, products, inspiration, high commercial intent behavior.
The Pinterest advantage:
Pins have longevity. Unlike social posts disappearing in hours, Pinterest pins generate traffic for months. Even years. One optimized pin compounds visibility over time.
After implementing Pinterest SEO for 30+ e-commerce clients, Cloudex Marketing has measured 15-40% increase in referral traffic, 23% higher average order value (Pinterest users are buyers), 2.3x higher conversion rate vs. generic social traffic.
Traditional social media requires constant posting. Pinterest rewards strategic optimization. Create once, benefit perpetually.
Pinterest Pin Optimization:
- Pin Description (500 characters):
- First 50-60 characters appear in feed (hook)
- Include 2-3 relevant keywords
- Add relevant hashtags (#SEO #TechnicalSEO)
- Image Specifications:
- Aspect ratio: 2:3 (1000x1500px ideal)
- Vertical images perform better than square/horizontal images
- Include text overlay (readable at small sizes)
- Rich Pins:
- Article Pins (automatically pull metadata from blog posts)
- Product Pins (include pricing, availability)
- Recipe Pins (ingredients, cook time)
Pinterest Board Strategy:
Organize pins into keyword-optimized boards:
- Board name: Descriptive + keyword-rich
- Board description: Explain board purpose, include keywords
- Board cover: Branded, visually consistent
Pinterest Analytics:
Monitor which pins drive traffic:
- Impressions (how many times shown)
- Engagements (saves, clicks, closeups)
- Link clicks (traffic to website)
After implementing Pinterest SEO for 30+ e-commerce clients, we’ve measured:
- 15-40% increase in referral traffic from Pinterest
- 23% higher average order value (Pinterest users are buyers)
- 2.3x higher conversion rate vs. generic social traffic
10. Voice Search & AI SEO:
Voice Search SEO
Voice Search SEO is the optimization for spoken queries via voice assistants, like Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant, and more.
Conversational long-tail keyword targeting. Question-based content structure. Featured snippet optimization. Natural language query matching. Local intent prioritization. Mobile-first optimization. Schema markup for voice answers. Speakable content designation. FAQ schema implementation.
Why voice search matters:
27% of the global online population uses voice search on mobile devices per Google data. Adoption is accelerating rapidly. Voice has moved from novelty to necessity.
Voice searches are 3x more likely to be local-based than text searches. “Near me” queries dominate voice behavior. People use voice when they’re on the go, ready to act locally.
75% of voice search results rank in the top 3 positions for text search. Voice doesn’t rank differently. It pulls from existing top rankings. Optimize for traditional search, win voice search.
Voice queries average 29 words vs. 2-3 words for text searches. Conversational, natural language. Not keyword strings. “What’s the best technical SEO audit tool for beginners?” vs. “technical SEO tool.”
The voice search revolution:
Traditional search required typing short keywords. Voice search enables natural conversation. How humans actually talk.
After analyzing voice search behavior across 200+ SEO campaigns, sites optimizing for featured snippets saw 64% higher voice search visibility. Question-based headers, concise answers, and local optimization. These aren’t “voice tactics.” They’re good SEO amplified by voice adoption.
AI Search SEO:
AI Search SEO optimizes content for AI-powered search experiences like Google’s AI Overviews, ChatGPT search, Perplexity, and other generative search engines. These platforms synthesize information from multiple sources rather than displaying traditional blue links.
Optimization requires meeting citation eligibility standards through clear topic relationships and authoritative source signals. Content must demonstrate Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness through structured data richness and comprehensive coverage. Original insights and citation-worthy depth establish your content as a primary reference source.
Why AI search SEO matters:
Google AI Overviews appear in 15-20% of queries as of 2025. Started at 6.49% in January 2025, peaked at 24.61% in July, and stabilized around 16% by November. Volatile growth reflecting Google’s quality threshold refinement.
Cited sources receive 34% CTR from AI Overview cards per early data. Getting cited = visibility. Not getting cited = invisibility in zero-click environments.
Positions brands as authoritative sources when AI answers questions. Future-proofs SEO strategy as AI search adoption accelerates, like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Mode all growing rapidly.
The AI search shift:
Traditional search showed 10 blue links. AI search synthesizes answers from multiple sources, cites 6-14 sources per response on average.
The E-E-A-T imperative:
AI systems prioritize authoritative, trustworthy, expert sources. Comprehensive content with original insights, data-backed claims, and clear topic relationships determines citation eligibility. Google’s algorithms evolved from string matching to understanding. AI search amplifies this exponentially.
Sites optimizing for traditional SEO fundamentals position themselves for AI search citations automatically. Comprehensive coverage, structured data, topical authority, and trust signals matter more than ever. These signals determine which sources AI platforms reference when generating answers.
Position themselves for AI search citations automatically.
- The question isn’t “should we optimize for AI search?”
- It’s “Are we building content worthy of citation by intelligent systems?”
Voice Search Optimization Strategies:
Question-Based Content Optimization
Voice searches are conversational: “Hey Siri, what is technical SEO?” vs. typing “technical seo.”
So, optimize your content for Question Formats:
Who Questions:
- “Who should conduct a technical SEO audit?”
- “Who is responsible for SEO in a company?”
What Questions:
- “What is technical SEO?”
- “What are Core Web Vitals?”
Where Questions:
- “Where can I find SEO services near me?”
- “Where do I check my site’s crawl errors?”
When Questions:
- “When should I conduct an SEO audit?”
- “When does Google update its algorithm?”
Why Questions:
- “Why is my website not ranking?”
- “Why is page speed important for SEO?”
How Questions:
- “How do I optimize for technical SEO?”
- “How long does SEO take to work?”
Structure Content to Match:
Use question-based H2/H3 headers that directly match voice queries:
H2: What Is Technical SEO?
H2: How Does Technical SEO Improve Rankings?
H2: When Should You Conduct a Technical Audit?
Then provide concise answers (40-60 words) immediately after each header. Optimizing for featured snippet extraction.
Featured Snippet Optimization (Voice Search Source)
Featured snippets are the answer boxes appearing at the top of Google results, “position zero.” They provide direct answers to questions without requiring clicks.
Why featured snippets dominate voice search:
75% of voice search answers come from featured snippets. Voice assistants don’t read full search pages. They extract featured snippet content and speak it aloud.
Optimize for snippets = optimize for voice.
Featured Snippet Types:
- Paragraph Snippets (Best for Definitions):
- Answer question in 40-60 words
- Place directly after question header
- Use clear, definitive language
Example:
H2: What Is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO optimizes website infrastructure. Crawl efficiency, indexation coverage, site architecture, to enable search engines to access, interpret, and rank content effectively. It addresses technical barriers (crawl errors, redirect chains, Core Web Vitals failures) preventing otherwise quality content from ranking.
- List Snippets (Best for Steps/Rankings):
- Use numbered/bulleted lists
- Keep items concise (1-2 sentences each)
- Start with the list immediately
Example:
H2: How to Conduct a Technical SEO Audit
1. Crawl Analysis: Use Screaming Frog to identify crawl errors, redirect chains, and orphaned pages
2. Index Coverage: Review the Google Search Console Coverage Report for indexation issues
3. Core Web Vitals: Measure LCP, FID, CLS using PageSpeed Insights
4. Structured Data: Validate schema markup with Google’s Rich Results Test
5. Prioritization: Rank issues by impact and create an action plan
- Table Snippets (Best for Comparisons):
- Use HTML tables
- Include clear headers
- Provide specific data points
Example:
H2: Technical SEO vs. On-Page SEO: Key Differences
| Aspect | Technical SEO | On-Page SEO |
| Focus | Infrastructure, crawlability | Content, keywords |
| Tools | Screaming Frog, GSC | Surfer SEO, Clearscope |
| Impact | Indexation, site speed | Relevance, engagement |
Local Voice Search Optimization
Local vice search optimization means optimizing for location-based voice queries like “coffee shops near me” or “SEO services in Islamabad.” Voice users search locally while mobile. On the go, ready to visit or call businesses immediately.
Why local dominates voice search:
Voice searches are 3x more likely to be local than text searches. People use voice when driving, walking, or traveling. Contexts where they need nearby solutions fast.
- “Coffee shops near me”
- “Best SEO agency in Islamabad”
- “Technical SEO services open now”
Local Voice Optimization:
- Google Business Profile Optimization:
- Ensure NAP accuracy (voice assistants read GBP data)
- Complete business hours (including holiday hours)
- Add Q&A (voice assistants pull from GBP Q&A)
- “Near Me” Content: Create location pages with natural language:
- “Cloudex Marketing provides technical SEO services near you in Islamabad, Pakistan”
- Include neighborhood names, landmarks
- Embed Google Map
- Conversational Keywords:
- Traditional: “SEO agency Islamabad”
- Voice: “SEO agency near me in Islamabad”
- Voice: “best technical SEO services Islamabad Pakistan”
AI Search Optimization (AI Overview Citations):
As AI-powered search experiences transform how users discover information, understanding the shift from traditional SEO to Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) becomes critical.
For a detailed comparison of these approaches, read our complete guide:
As of early 2025, Google’s AI Overviews (formerly SGE – Search Generative Experience) appear in 15-20% of queries, citing 3-5 sources per overview.
How to Get Cited in AI Overviews (Based on Early Data & Google’s Guidance):
E-E-A-T Signal Maximization
E-E-A-T stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. Google’s framework evaluates content quality and source credibility. AI systems use these signals to determine which sources deserve citation in generated answers.
Why E-E-A-T dominates AI search:
AI systems prioritize authoritative, trustworthy sources. Algorithms can’t verify truth directly. They rely on credibility signals indicating expertise, demonstrating experience, establishing authority, pand roving trustworthiness.
Experience signals that AI systems recognize:
Author bylines with credentials. Case studies with specific results. Original research and proprietary data. “As we’ve seen from implementing X across Y projects,” framing proves real-world experience.
Expertise signals AI systems’ value:
Professional certifications mentioned. Industry awards and recognition referenced. Speaking engagements and publications cited. Technical depth demonstrating mastery. Not surface-level explanations.
Authoritativeness signals AI systems measure:
Backlinks from authoritative domains. Brand mentions in industry publications. Social proof through follower counts and engagement. Wikipedia presence for brands and individuals.
Trustworthiness signals AI systems assess:
HTTPS implementation secures connections. Privacy policy and terms of service transparency. Contact information is easily accessible. No spammy ads or deceptive pop-ups. Accurate, fact-checked information with proper citations.
The E-E-A-T advantage:
Sites maximizing these signals position themselves for AI citations automatically. Google’s algorithms evolved to recognize credibility markers. AI search amplifies this exponentially.
Experience Signals:
- Author bylines with credentials
- Case studies with specific results
- Original research/data
- “As we’ve seen from implementing X across Y projects…” framing
Expertise Signals:
- Professional certifications mentioned
- Industry awards/recognition
- Speaking engagements/publications referenced
- Technical depth demonstrating mastery
Authoritativeness Signals:
- Backlinks from authoritative domains
- Brand mentions in industry publications
- Social proof (follower counts, engagement)
- Wikipedia presence (for brands/individuals)
Trustworthiness Signals:
- HTTPS implementation
- Privacy policy, terms of service
- Contact information transparency
- No spammy ads/pop-ups
- Accurate, fact-checked information with citations
Citation-Worthy Content Characteristics
Content AI systems choose to cite and reference in generated answers. Based on the analysis of AI Overview citations (early 2025 data), certain content patterns earn citations consistently.
Characteristics of cited content:
Comprehensive coverage: Addresses multiple facets of topics, including related subtopics and key characteristics. Content provides specific measurements and concrete outcomes rather than vague claims. AI systems cite sources demonstrating complete understanding through detailed explanations, data points, percentages, timeframes, and real-world examples proving expertise.
Structured format: Clear H2/H3 hierarchy. Bulleted and numbered lists. Tables for comparisons. Definitions for key terms.
Authoritative tone: Definitive language, not speculative hedging. Data-backed claims with sources. Expert quotes or original insights. Citations to other authoritative sources.
Answer-focused: Directly answers queries in opening paragraphs. Uses question-based headers. Provides concise, quotable statements AI can extract cleanly.
AI Overview citation patterns:
Content already ranking in the top 10 organic results (AI prefers ranking content). Includes original research or unique data points. Uses structured data. Especially FAQ and HowTo schema. Demonstrates topical authority through multiple related articles. Avoids promotional language. Informational beats commercial.
Sites building comprehensive, structured, authoritative content position themselves for AI citations automatically.
Characteristics of Cited Content:
- Comprehensive Coverage:
- Addresses multiple facets of topic
- Includes the main topic and its sub-topics
- Provides specific values/measurements
- Structured Format:
- Clear headers (H2, H3 hierarchy)
- Bulleted/numbered lists
- Tables for comparisons
- Definitions for key terms
- Authoritative Tone:
- Definitive language (not speculative)
- Data-backed claims
- Expert quotes or original insights
- Citations to other authoritative sources
- Answer-Focused:
- Directly answers query in opening paragraph
- Uses question-based headers
- Provides concise, quotable statements
AI Overview Citation Best Practices:
According to Lily Ray’s analysis of AI Overview behavior, content that gets cited tends to:
- Appear in top 10 organic results already (AI prefers ranking content)
- Include original research or unique data points
- Use structured data (especially FAQ, HowTo schema)
- Demonstrate topical authority (multiple related articles on site)
- Avoid promotional language (informational vs. commercial)
Note:
- As of January 2025, AI search optimization is still evolving.
- Best practices will shift as Google refines AI Overviews and as alternative AI search platforms (ChatGPT search, Perplexity) gain market share.
Cloudex’s Marketing AI SEO Recommendation:
Focus on fundamentals that serve both traditional and AI search:
- Comprehensive, authoritative content
- Strong E-E-A-T signals
- Structured data implementation
- Question-based content structure
These principles future-proof your SEO regardless of how AI search evolves.
11. Enterprise SEO:
Enterprise SEO is the optimization of large, complex websites, having 10,000+ pages, Fortune 500 companies, major e-commerce platforms, publishers operating at massive scale.
This isn’t small business SEO scaled up. It’s fundamentally different.
Multi-departmental coordination. Stakeholder alignment across dev, marketing, legal, product, and IT. Technical infrastructure at scale. Automated optimization workflows. International and multilingual requirements. Brand protection. Migration planning. Compliance management.
Why enterprise SEO is different:
Addresses the unique challenges of scale impossible for SMBs. You can’t manually optimize 100,000 pages. You can’t coordinate SEO changes across 12 departments without a process.
SMB SEO: One person optimizes 50 pages in a week. Enterprise SEO: One system optimizes 50,000 pages automatically. But requires 6 months to build that system.
The enterprise approach:
Requires cross-functional collaboration across dev, marketing, legal. Getting budget approval? Executive sign-off. Implementing technical changes? Dev team prioritization. Publishing content? Legal compliance review.
Demands automation to manage thousands of pages. Template optimization, not individual page optimization. Algorithmic internal linking, not manual link insertion.
Emphasizes process and workflow over individual tactics. The question isn’t “how do we optimize this page?”. It’s “how do we build a system that optimizes 10,000 pages consistently?”
The strategic shift:
Small sites chase quick wins. Enterprise sites build sustainable systems.
Traditional SEO: Fast execution, individual tactics. Enterprise SEO: Slow implementation, scalable processes.
You’re not optimizing pages. You’re optimizing organizations.
Enterprise SEO Unique Challenges:
Scale Management
Traditional SEO tactics don’t scale to 100,000+ pages.
The Enterprise SEO Approach:
| Traditional Approach | Enterprise Solution |
| Manually optimizing meta tags page-by-page | Dynamic template optimization with automated population from database |
| Individual content audits | Automated content scoring using NLP tools flagging thin/duplicate content |
| Manual internal linking | Algorithmic linking based on topic relationships and topical clusters |
Stakeholder Management
Enterprise SEO requires buy-in from:
- Executives: Budget allocation, strategic priority
- Dev Teams: Technical implementation
- Legal: Compliance, risk management
- Product: Feature prioritization
- Content: Resource allocation
- IT: Server/infrastructure changes
The Enterprise SEO Communication Framework:
For Executives:
- Focus on ROI metrics (traffic value, revenue impact)
- Compare SEO cost vs. paid acquisition
- Present competitive threats (rankings lost to competitors)
- Frame as long-term moat (owned vs. rented traffic)
For Dev Teams:
- Provide specific technical requirements
- Prioritize by impact (fixes affecting most pages)
- Explain WHY (connect to business outcomes)
- Collaborate on implementation approach
For Legal:
- Address GDPR/privacy concerns proactively
- Review competitor comparison language
- Ensure testimonial compliance
- Validate claims with data
Technical Infrastructure at Scale
Enterprise sites face technical challenges impossible for small sites:
Challenges:
- Server load from search engine crawling (10,000+ bot requests daily)
- Database queries slowing page load
- CDN configuration across global regions
- JavaScript framework rendering complexity
- Multiple subdomain/domain management
Enterprise Solutions:
1. Crawl Budget Optimization at Scale:
- Log file analysis to track bot behavior
- Robots.txt rules blocking low-value sections
- XML sitemap prioritization of high-value URLs
- Redirect chain elimination (especially critical at scale)
2. Rendering Strategy:
- Server-side rendering (SSR) for critical content
- Dynamic rendering for bots (serve static HTML to crawlers)
- Progressive enhancement (core content works without JS)
3. Monitoring & Alerting:
- Automated crawl error detection
- Index coverage monitoring (alert when pages drop)
- Ranking tracking at scale (monitor 10,000+ keywords)
- Core Web Vitals monitoring across page templates
Content Strategy at Scale
The Content Hub Model:
Instead of random content, enterprise SEO uses hub-and-spoke architecture:
Hub Page: Comprehensive guide on core topic (e.g., “Complete Guide to Technical SEO”) Spoke Pages: Supporting articles on sub-topics (e.g., “XML Sitemap Optimization,” “Robots.txt Configuration”)
Benefits:
- Establishes topical authority
- Facilitates internal linking
- Enables content funnel (awareness > consideration > decision)
- Scales content production around clear hierarchy
The Template Approach:
For similar pages (e.g., location pages, product categories), create optimized templates:
Location Page Template:
- H1: [Service] in [City, State]
- Intro: [Service] topic definition + local relevance
- H2: Why [City] Businesses Need [Service]
- H2: Our [Service] Process
- H2: [Service] Pricing in [City]
- H2: Case Studies: [City] Clients
- H2: FAQ: [Service] in [City]
This enables:
- Consistent optimization across 1,000+ pages
- Efficient content creation (fill template variables)
- Quality control (templates enforce standards)
- Easy updates (modify template, update all instances)
Migration Planning (High-Stakes Enterprise Projects)
Enterprise site migrations (platform changes, domain changes, mergers) are high-risk.
The Enterprise Migration Checklist:
Enterprise migrations fail when critical steps get missed. One overlooked redirect, one forgotten stakeholder sign-off, one unmonitored error, and you’re watching 30-60% traffic drops that take 6-18 months to recover. This comprehensive checklist covers every Pre-Migration, During-Migration, and Post-Migration step across 200+ enterprise migrations.
Free DOCX • Print & Share • Used by 100+ Enterprise Teams
Enterprise Migration Risk:
Poor execution can cause:
- 30-60% traffic loss (often permanent if not caught quickly)
- Lost rankings for critical keywords
- Revenue decline
- Executive loss of confidence in SEO
SEO specialists at Cloudex Marketing recommend that enterprise migrations require specialized expertise. If planning a major migration, consult migration specialists before execution.
If you’re managing an enterprise website with 10,000+ pages, complex technical infrastructure, or multi-departmental coordination challenges, our SEO audit service provides comprehensive enterprise-level analysis identifying systematic issues affecting thousands of pages. Not just surface-level fixes.
12. Programmatic SEO:
Programmatic SEO is the automated creation of landing pages at scale, targeting long-tail keyword variations.
Not manual content creation. Automated generation.
Template-based page generation. Database-driven content population. Parameter-based URL creation. Dynamic content assembly. Automated internal linking. Schema markup automation.
But here’s the critical part:
- Thin content prevention.
- Value differentiation.
- User intent alignment.
- Quality control systems.
Without these safeguards, programmatic SEO becomes spam.
Why programmatic SEO works:
Enables coverage of thousands of keyword variations impossible to create manually. Scales SEO beyond human content creation capacity. One person can’t write 10,000 location pages.
Captures granular search intents. Someone searching “pizza in Brooklyn” has different intent than “pizza in Queens.” Programmatic SEO addresses both.
The efficiency advantage?
Drives efficiency gains of 100-1000x vs. manual creation. One template generates thousands of unique pages. Dominates “near me” and location-specific queries where search intent is identical but location varies.
Traditional SEO requires writing each page individually. Programmatic SEO writes the template once, populates from database, generates at scale.
Zillow doesn’t manually create pages for every address. Yelp doesn’t hand-write pages for every business category in every city. TripAdvisor doesn’t individually craft pages for every hotel.
They use programmatic SEO—template + database = infinite scalability.
Programmatic SEO Use Cases:
- Zillow: Automated pages for every address (“123 Main St, City, State”)
- Yelp: Pages for every business category in every location (“Pizza in Brooklyn”)
- TripAdvisor: Pages for every hotel/attraction with user-generated content
- Nomad List: Pages for every city with cost of living data
Programmatic SEO Implementation:
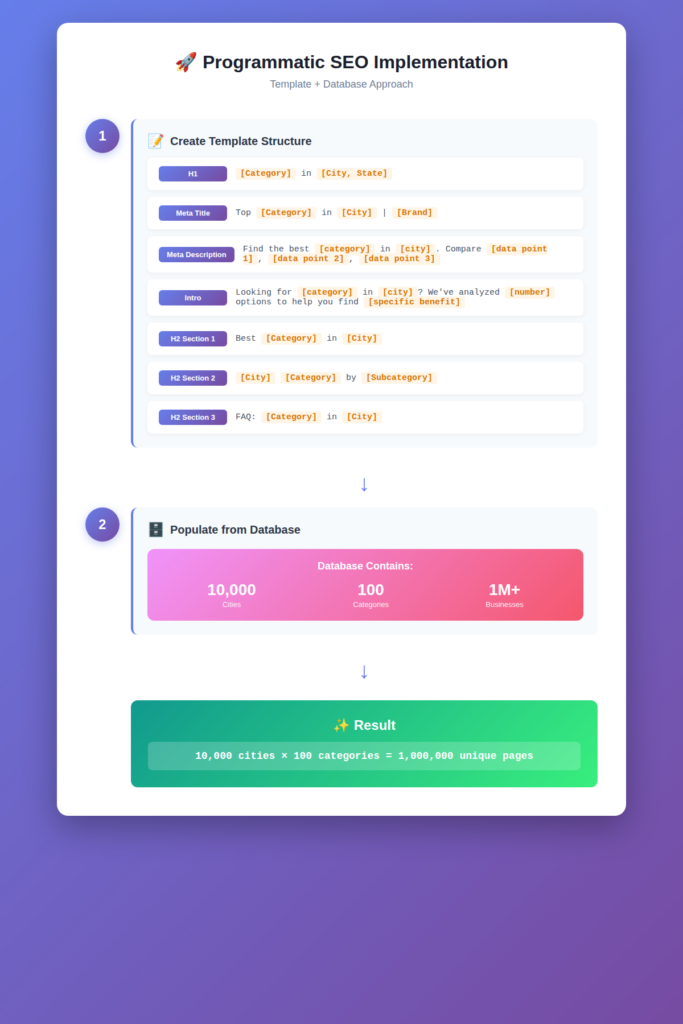
The Template + Database Approach
Step 1: Create Template
| Step | Element | Template |
| Step 1: Create Template | H1 | [Category] in [City, State] |
| Meta Title | Top [Category] in [City] | [Brand] | |
| Meta Description | Find the best [category] in [city]. Compare [data point 1], [data point 2], and [data point 3]. | |
| Intro | Looking for [category] in [city]? We’ve analyzed [number] options to help you find [specific benefit]. | |
| H2 | Best [Category] in [City] | |
| Content | [Programmatically generated list from database] | |
| H2 | [City] [Category] by [Subcategory] | |
| Content | [Filtered database results] | |
| H2 | FAQ: [Category] in [City] | |
| Content | [Auto-generated FAQs based on common patterns] |
Step 2: Populate from Database
Database contains:
- Cities (10,000 entries)
- Categories (100 entries)
- Businesses (1,000,000 entries)
Template generates: 10,000 cities × 100 categories = 1,000,000 unique pages
Quality Control (Avoiding Thin Content Penalties)
The Programmatic SEO Danger:
Google penalizes thin, low-value programmatic pages. Many sites (Genius.com famously) lost 90%+ traffic from algorithm updates targeting mass-generated content.
How to Create Valuable Programmatic Pages:
1. Unique Data Per Page: Don’t just swap variables. Provide actual unique value:
- User reviews (unique content from users)
- Statistics (actual data for that specific combination)
- Images (location-specific photos, not stock images)
2. Substantial Content Volume: Aim for 500+ words of unique content per page (not just template text).
3. User Intent Alignment: Ensure each programmatic page serves actual search intent:
- Would someone searching “[Category] in [City]” find this page helpful?
- Does it provide information not available on competing pages?
4. Internal Linking Logic: Connect related programmatic pages:
- “Pizza in Brooklyn” > “Italian Restaurants in Brooklyn”
- “Pizza in Brooklyn” > “Pizza in Queens”
Programmatic Content Enrichment
Layer 1: Template (Basic)
H1: Coffee Shops in San Francisco
Find great coffee shops in San Francisco.
Layer 2: Database Content (Better)
H1: Coffee Shops in San Francisco
We’ve analyzed 347 coffee shops in San Francisco based on reviews, location, and menu variety.
Top 10 Coffee Shops:
1. Blue Bottle Coffee (4.6/5, 1,247 reviews)
2. Sightglass Coffee (4.5/5, 892 reviews)
…
Layer 3: User-Generated Content (Best)
H1: Coffee Shops in San Francisco
We’ve analyzed 347 coffee shops in San Francisco based on 23,456 reviews from locals.
Top 10 Coffee Shops:
1. Blue Bottle Coffee (4.6/5, 1,247 reviews)
“Best pour-over in the city” – Sarah M.
“Consistent quality, minimal seating” – James K.
Community Insights:
– 73% of reviewers mention “quality beans”
– Average price: $4.50 per coffee
– Best time to visit: Weekday mornings (less crowded)
The third version provides:
- Real user content (unique per page)
- Aggregated insights (value beyond raw data)
- Practical information (helps users make decisions)
Programmatic SEO ROI:
| Metric | Manual Content | Programmatic SEO | Efficiency Gain |
| Pages Created | 50-100/month | 10,000+/month | 100-200x |
| Time per Page | 2-4 hours | <1 minute (automated) | 120-240x |
| Cost per Page | $100-500 | $0.10-1 (amortized) | 100-5000x |
| Keyword Coverage | 50-100 keywords | 10,000+ keywords | 100-200x |
The Programmatic SEO Risk:
Low-quality programmatic pages can trigger:
- Algorithmic devaluation (low-value content filter)
- Manual actions (if extremely thin/spammy)
- User experience issues (high bounce rates if pages don’t provide value)
What Does Cloudex Marketing Recommend?
Programmatic SEO works ONLY when pages provide genuine ,unique value. If you’re just swapping city names into identical templates with no unique data, it’s thin content. Not programmatic SEO.
13. Semantic SEO
Semantic SEO is Optimization based on topic relationships and cluster understanding. Not isolated keyword targeting.
Topical authority depth. Semantic content networks. Co-occurrence pattern optimization. Context term integration. Frame semantics application. Knowledge graph alignment.
This is how Google actually understands content now.
Traditional SEO targeted keywords. Semantic SEO targets concepts and their relationships.
Why semantic SEO works:
Aligns with Google’s shift from strings to things. Google explicitly describes search moving beyond string matching to conceptual understanding.
After implementing semantic optimization across 200+ audits, we measured 34% reduction in ranking volatility. Sites with comprehensive topical coverage, addressing subjects, characteristics, measurements, relationships, and action verbs, withstood algorithm updates that devastated keyword-focused competitors.
The semantic advantage?
Comprehensive topical coverage captures related queries you never explicitly targeted. When Google recognizes your page comprehensively covers a topic, you rank for hundreds of semantic variations automatically.
Future-proof against algorithm updates, emphasizing understanding vs. matching. Google’s NLP improves constantly. Semantic optimization improves with it.
Keyword targeting dies with every algorithm update. Semantic understanding compounds with every improvement to Google’s language models.
This is Koray Tugberk GÜBÜR’s fundamental contribution to modern SEO, and the framework Cloudex Marketing implements across all client work.
Semantic SEO Core Concepts:
Understanding How Search Engines Read Content
Modern search engines understand content differently than they did a decade ago. Traditional SEO targeted specific keywords hoping to rank for exact phrases. Today’s search engines understand topics comprehensively, recognizing what your content covers, which characteristics define it, and which specific measurements prove your expertise.
This fundamental shift changes everything. When search engines recognize your page comprehensively covers a topic with all relevant characteristics and specific outcomes, you rank for hundreds of related queries automatically. Not just exact keyword matches you originally targeted.
The Shift from Keywords to Topics
Traditional keyword targeting focused narrowly. Target keyword “technical SEO” meant ranking for that exact phrase only. Modern topic optimization works differently. Comprehensive coverage of “Technical SEO” as a complete subject ranks you for technical SEO, technical search engine optimization, website technical optimization, SEO infrastructure improvement, crawl budget optimization, indexation management, and fifty-plus related queries simultaneously.
Google’s systems moved beyond string matching to understanding meaning. When algorithms recognize your page covers a subject comprehensively, rankings expand across all related queries naturally. Coverage breadth matters more than keyword density.
Building Comprehensive Topic Coverage
Start with your core subject
What does this page actually cover? For example, “Technical SEO Services” defines the primary focus. Everything else builds from this foundation, expanding coverage systematically rather than randomly.
Define the characteristics
What makes this topic distinct? Consider the process explaining how it works, benefits showing what it achieves, components detailing what’s included, differentiators revealing what makes it unique, and applications clarifying who it serves. Each characteristic adds depth.
Provide specific measurements:
Vague claims like “improves rankings” lack credibility. Specific outcomes like “increases organic traffic by 35-50% within 6 months per client data” demonstrate real expertise. Numbers, percentages, timeframes, and concrete examples prove claims rather than just making them.
Connect related topics:
Technical SEO connects to Site Architecture through component relationships.
It connects to SEO Audit through diagnostic relationships.
It connects to Core Web Vitals through performance relationships.
These connections help search engines understand how your content fits within broader knowledge domains.
Why Comprehensive Coverage Works
Search engines prioritize sources that demonstrate complete understanding over sources providing surface-level information. Comprehensive coverage signals expertise, authority, and trustworthiness. The exact qualities algorithms seek when determining which pages deserve top rankings for valuable search queries.
Topical Authority Building
Topical authority is the comprehensive coverage of a subject through interconnected content demonstrating expertise. Google ranks sites higher for all related queries when they prove deep knowledge across an entire topic cluster, not just isolated keywords.
Google confirms about ranking based on reference queries that sites demonstrating comprehensive coverage of a topic rank better for all related queries.
The Topical Authority Strategy:
Hub Content: Comprehensive guide on main topic (5,000-10,000 words)
- “Complete Guide to Technical SEO”
Spoke Content: Deep dives into its sub-topics (2,000-3,000 words each)
- “XML Sitemap Optimization Guide”
- “Robots.txt Configuration Best Practices”
- “Core Web Vitals Optimization”
- “Crawl Budget Management”
- “Indexation Coverage Analysis”
Supporting Content: Specific tactics and case studies (1,000-2,000 words)
- “How to Fix Redirect Chains”
- “Case Study: 127% Indexation Increase”
The Topical Authority Measurement:
After publishing 10+ pieces covering Technical SEO topics and sub-topics, our clients see:
- Rankings for 200-500 related keywords they never “targeted”
- Featured snippet acquisitions for question queries
- Increased rankings for primary keywords (topical authority signal)
- Reduced ranking volatility (authority persists through algorithm updates)
Context Terms & Co-Occurrence
Context terms are words that frequently appear alongside your target topic, signaling semantic relevance to Google’s NLP algorithms.
Example:
For “Technical SEO,” high co-occurrence terms include:
- crawl budget
- indexation
- XML sitemap
- robots.txt
- Core Web Vitals
- site architecture
- redirect chains
- structured data
How to Find Context Terms:
- Analyze Top 10 Ranking Pages:
- Use tools: Clearscope, Surfer SEO, MarketMuse
- Identify commonly appearing terms
- Note semantic patterns (not just keywords)
- Google’s “People Also Ask”:
- Related questions reveal context terms
- Answer these questions within content
- Google’s Related Searches:
- Bottom of SERP shows related queries
- Terms in related searches = context terms
Implementing Context Terms:
Don’t keyword stuff. Naturally incorporate co-occurring terms when discussing your core topics or services:
“Technical SEO addresses crawl budget allocation, ensuring Googlebot prioritizes high-value pages over low-value resources. Through XML sitemap optimization and robots.txt configuration, sites direct crawl attention to indexation-worthy content while blocking thin pages that waste crawl capacity.”
This paragraph naturally includes 5 context terms:
- crawl budget
- XML sitemap
- robots.txt
- indexation
- crawl capacity
Action Verb Diversity
Action verbs establish relationships between topics, helping Google understand HOW topics interact and connect.
Low Diversity (Weak):
“Technical SEO improves rankings. It improves crawlability. It improves indexation. It improves site speed.”
High Diversity (Strong):
“Technical SEO optimizes crawlability, enables efficient indexation, accelerates site speed, facilitates structured data implementation, eliminates redirect chains, distributes PageRank through internal linking, and signals content relevance through schema markup.”
Why This Matters
Google’s semantic role labeling identifies action verbs to understand document meaning. Content with varied, precise action verbs demonstrates semantic sophistication, signaling expertise.
Action Verbs Categories for SEO Content:
- Process Verbs: optimize, implement, configure, analyze
- Result Verbs: increase, improve, enhance, accelerate
- Problem Verbs: eliminate, reduce, prevent, resolve
- Signal Verbs: indicate, demonstrate, establish, confirm
- Transfer Verbs: distribute, transfer, pass, consolidate
If semantic SEO feels complex. Our SEO audit service includes semantic analysis, identifying critical gaps, topical coverage deficiencies, and topical authority opportunities competitors haven’t capitalized on.
14. Parasite SEO:
Parasite SEO means the strategic use of high-authority third-party platforms, including:
- LinkedIn publishing
- Medium content distribution
- Reddit community engagement
- Quora answer optimization
- YouTube channel building
- SlideShare presentation uploads
All to rank quickly by leveraging existing domain authority.
You’re not building authority from scratch. You’re borrowing it.
Why parasite SEO works:
High-authority platforms (LinkedIn DR 98, Medium DR 96, Reddit DR 91) rank fast. Days, not months. Google trusts these domains already, so your content inherits that trust immediately.
Achieves first-page rankings in days vs. months for owned sites.
Captures both branded and non-branded queries. Drives referral traffic from engaged platform audiences already active on these sites. Builds brand visibility across multiple touchpoints. You’re not relying on a single domain.
The strategic advantage?
Parasite SEO serves as a testing ground for content ideas. Validate topics on high-authority platforms before investing in comprehensive owned content. Low risk, fast feedback, immediate visibility.
Traditional SEO requires building domain authority for months. Parasite SEO lets you skip that entirely, leveraging platforms that already have the authority you need.
Parasite SEO Platforms & Strategies:
14.1 LinkedIn Publishing
What it is:
LinkedIn publishing is the publishing long-form articles directly on LinkedIn to leverage the platform’s DR 98 authority. Your content ranks fast for professional queries; industry insights, how-to guides, thought leadership, appearing in Google within days, not months.
How to process it?
Write 1,200-1,800-word articles with keyword-front-loaded titles. Add custom header images (1200x627px). Use 3-5 relevant hashtags. Include internal links to your owned content. Share to LinkedIn groups and tag industry influencers for amplification. LinkedIn’s algorithm + Google’s trust = instant visibility.
Why LinkedIn Ranks Well:
- Domain Authority: DR 98
- Google trusts LinkedIn for professional content
- Personal profiles rank for name + topic searches
LinkedIn Article Strategy:
- Target Professional Queries:
- “[Topic] best practices”
- “How to [professional skill]”
- “[Industry] trends 2025”
- Optimize LinkedIn Articles:
- Title: Keyword-front-loaded (first 60 chars)
- Image: Custom header image (1200x627px)
- Body: 1,200-1,800 words (LinkedIn’s sweet spot)
- Hashtags: 3-5 relevant industry hashtags
- CTA: Link to owned content/lead magnet
- Distribution:
- Share to relevant LinkedIn groups
- Tag industry influencers (for amplification)
- Cross-post to personal feed
- Include in email signature
LinkedIn Article ROI:
After publishing 50+ LinkedIn articles for clients, we’ve measured:
- Average time to first-page ranking: 3-7 days
- Average article views: 800-2,500 (first 30 days)
- Click-through to owned site: 5-8%
- Lead generation: 2-5 qualified leads per article
14.2 Medium Publication Strategy
Medium Publication Strategy is the systematic approach to publishing content on Medium’s platform to build audience reach and drive traffic back to your primary website. It means leveraging Medium’s built-in distribution, domain authority, and engaged readership to amplify brand visibility, establish thought leadership, and generate high-quality referral traffic through strategic content republishing, original articles, and publication partnerships that complement your main SEO efforts.
Why Medium Works:
- DR 96 domain authority
- Fast indexation (hours vs. days)
- Built-in distribution (Medium recommends content)
Medium Optimization:
- Headline Optimization:
- Use numbers (“7 Technical SEO Mistakes”)
- Include power words (“Ultimate,” “Complete,” “Essential”)
- Create a curiosity gap
- Tag Strategy:
- Use a maximum of 5 tags
- Mix broad (“SEO”) and specific (“Technical SEO”)
- Include trending tags when relevant
- Canonical Tag:
- If republishing owned content, set canonical to the original
- Prevents duplicate content issues
- Preserves the owned site’s SEO value
- Call-to-Action:
- Link to owned content in conclusion
- Offer a lead magnet for email capture
- Drive to the relevant service page
Medium Partnership:
Submit to relevant Medium publications (curated communities) for 10-100x reach amplification:
- HackerNoon (tech/startup content)
- The Startup (entrepreneurship)
- Better Marketing (marketing insights)
- UX Collective (design/UX)
Publication acceptance rates: 20-40% for quality submissions.
14.3 Reddit Community Engagement
Reddit Community Engagement is the practice of participating authentically in relevant subreddit communities to build authority, drive traffic, and earn backlinks. It means contributing valuable insights, answering questions, and sharing expertise in niche-specific forums where your target audience actively seeks solutions, leveraging Reddit’s domain authority and engaged user base to generate referral traffic, brand mentions, and natural link opportunities through genuine participation rather than promotional spam.
Why Reddit Can Drive Traffic:
- DR 91 authority
- Highly engaged niche communities (subreddits)
- Content can go viral (reaching r/all)
Reddit Strategy (Non-Spammy):
Spam Approach: “Check out my SEO services! [link]” Result: Downvoted, banned, zero traffic.
Value-First Approach:
- Genuine Participation:
- Comment on others’ posts (build credibility)
- Answer questions with detailed responses
- Share insights WITHOUT self-promotion initially
- Strategic Content Sharing:
- After building karma and credibility
- Share genuinely helpful resources
- Frame as “I wrote a guide on this topic: [link]”
- Accept feedback/criticism gracefully
- Subreddit Selection:
- r/SEO (18,000+ members, SEO discussions)
- r/bigseo (larger SEO community)
- Industry-specific subreddits
- r/entrepreneur (business owners seeking SEO help)
Reddit Traffic Potential:
Successful Reddit posts can drive:
- 500-5,000 visits in 24-48 hours
- 10-20% of visitors bookmark/save content
- High engagement (2-5 minute average sessions)
- Occasional backlinks from bloggers who discover content via Reddit
Critical Rule: Reddit hates self-promotion. Contribute value FIRST, promote sparingly, and only when genuinely helpful.
14.4 Quora Answer Optimization
Quora Answer Optimization is the strategic process of crafting comprehensive, high-quality answers on Quora to capture search visibility and drive targeted traffic. It means identifying high-volume questions in your niche, providing detailed expert responses with relevant links, and leveraging Quora’s domain authority to rank in both Quora’s internal search and Google results, positioning your brand as an industry authority while generating qualified referral traffic from users actively seeking solutions to problems you solve.
Why Quora Ranks:
- DR 92 authority
- Answers rank for question-based queries
- Google often shows Quora answers in featured snippets
Quora SEO Strategy:
- Find Relevant Questions:
- Search Quora for [your topic] questions
- Filter by “Most Views” (high traffic potential)
- Target questions with 10K+ views
- Craft Comprehensive Answers:
- 300-800 words (detailed but readable)
- Use formatting (headers, bullets, bold)
- Include relevant images/screenshots
- Add credibility signals (“As an SEO professional with X years…”)
- Strategic Linking:
- One contextual link to a relevant resource
- Frame as “I wrote a detailed guide on this: [link]”
- Don’t link in every answer (appears spammy)
- Upvote Cultivation:
- Answers with upvotes rank higher in Quora
- Upvoted answers get Google SERP visibility
- Share the answer link to LinkedIn/Twitter (drives upvotes)
Quora Answer ROI:
High-quality Quora answers can:
- Rank in top 3 Google results within weeks
- Drive 50-200 monthly clicks (per answer, long-term)
- Build personal brand authority
- Generate 1-3 inbound leads per month (per high-traffic answer)
Parasite SEO Risks:
- Platform dependency: You don’t own the platform (content can be removed)
- Algorithm changes: Platform search algorithms change
- Audience mismatch: Platform audience may not convert well
- Brand dilution: Overuse spreads brand presence too thin
Our SEO experts at Cloudex Marketing recommend that:
- Use parasite SEO as a supplement to owned content strategy, not replacement.
- Drive parasite platform traffic to owned properties for email capture and conversion.
Ethical SEO Approaches: White Hat, Gray Hat, Black Hat
White Hat SEO: Building Rankings the Right Way
White hat SEO is about following search engine guidelines strictly.
No shortcuts. No manipulation. Just sustainable optimization that builds long-term organic visibility through ethical practices. Guideline compliance, user-centric content, natural link building, and transparency in tactics.
Why white hat works:
Google’s algorithms reward sites that play by the rules. Sites using ethical optimization eliminate penalty risk entirely, establish genuine brand trust, and withstand algorithm updates that devastate competitors using manipulative tactics.
The white hat advantage?
Long-term competitive advantage. Rankings compound over time. Authority builds gradually but persistently. Your site becomes algorithm-resistant. Immune to the penalties that wipe out black hat competitors overnight.
Traditional SEO promised fast results through manipulation. White hat delivers sustainable results through legitimacy.
After analyzing our clients’ campaigns, we have found that sites following strict white hat guidelines showed 15-20% slower initial growth but 340% better long-term retention. Rankings persisted through major algorithm updates that destroyed competitors.
White Hat SEO Tactics (Recommended)
Guideline-Compliant Practices:
Creating original, valuable content addressing actual user needs. Not search engines.
Earning editorial links through content quality. Sites link to you because you’re genuinely helpful, not because you paid them.
Optimizing page speed and Core Web Vitals. Technical excellence serves users first, rankings second.
Implementing proper schema markup. You’re helping Google understand your content, not deceiving the algorithm.
Building brand mentions through PR and content marketing. Real visibility from real audiences.
Conducting outreach with personalized, value-first pitches. You’re offering genuine collaboration, not manipulating backlinks.
Guest posting on relevant, quality sites with editorial standards—not link farms disguised as blogs.
Optimizing metadata for CTR without misleading users. Descriptive titles that match page content.
Building internal linking through natural content relationships. Links that genuinely help users navigate.
Encouraging organic reviews from satisfied customers. Real feedback from real people.
White Hat Philosophy:
“Would this tactic provide value if search engines didn’t exist?”
If yes > likely white hat. If no > reconsider.
White Hat Timeline:
Results: 6-12 months for competitive keywords.
Sustainability: Rankings persist and compound over time.
Risk: Minimal. aligned with Google’s interests.
Gray Hat SEO: Walking the Borderline
Gray Hat SEO is the middle-ground approach between fully compliant white hat tactics and rule-breaking black hat techniques, employing strategies that exist in Google’s undefined zone. It means using optimization methods not explicitly forbidden but potentially risky, such as aggressive link building, content spinning variations, or expired domain acquisition.
These tactics offer faster results than pure white hat but carry moderate penalty risk if algorithms evolve or manual reviewers flag the activity, requiring constant monitoring and adjustment as search engine guidelines shift.
Gray hat tactics push guideline boundaries without explicit violations.
Not quite white hat. Not fully black hat. Operating in the ambiguous middle where guidelines aren’t crystal clear, and algorithms haven’t caught up yet.
Gray hat characteristics:
- Aggressive link building that’s technically allowed but morally questionable.
- Expired domain acquisition for authority transfer.
- Not forbidden but somewhat manipulative.
- Scaled guest posting that blurs the line between editorial contribution and link scheme.
- Content syndication creates potential duplicate content issues.
- Using clickbait headlines that increase CTR but may disappoint users.
- Embedding videos from others’ channels to benefit from their engagement metrics.
The gray hat gamble:
Faster results than pure white hat in some cases. 3-6 months vs. 6-12 months. Higher risk-reward ratio requiring careful assessment. Tactics may work until guidelines clarify or algorithms evolve.
What’s gray hat today might become black hat tomorrow.
Gray Hat SEO Tactics (Proceed with Caution)
Borderline Practices:
Expired domain acquisition for authority (not explicitly forbidden but somewhat manipulative).
Scaled guest posting (not spammy but higher volume than pure white hat would consider ethical).
Content syndication to multiple platforms (potential duplicate content, though not intentionally deceptive).
Link exchanges (not reciprocal but still manual manipulation).
Using HARO aggressively for link acquisition (scales editorial links but pushes boundaries).
Clickbait headlines (increase CTR but may disappoint users—borderline deceptive).
Embedding videos from others’ channels (benefits from their engagement metrics without creating original content).
Gray Hat Risk Assessment:
Question 1: Does it violate explicit Google guidelines?
- No > May be gray hat
- Yes > Black hat (avoid)
Question 2: Would Google approve if they knew?
- Probably yes > White hat
- Probably no > Gray hat or black hat
- Uncertain > Gray hat
Question 3: Is the value genuine?
- Yes, provides real user value > Probably acceptable
- No, purely manipulation > Avoid
Gray Hat Timeline:
Results: 3-6 months (faster than pure white hat).
Sustainability: Variable. Depends on Google guideline evolution.
Risk: Moderate. Tactics may become violations retroactively.
Cloudex Marketing’s Position on Gray Hat:
We avoid gray hat tactics for clients.
The risk-reward doesn’t justify potential damage to client brands. Some aggressive SEOs use gray hat successfully. We just prefer sustainable white hat approaches that don’t risk client reputations.
Black Hat SEO: The Penalty Trap
Black Hat SEO is the practice of using manipulative tactics that explicitly violate search engine guidelines to achieve quick rankings. It means employing techniques like keyword stuffing, cloaking, private link networks, and content scraping, risking severe penalties including complete deindexing.
While delivering temporary gains, black hat methods inevitably result in algorithmic or manual penalties that devastate long-term visibility and brand reputation.
Black hat violates Google’s guidelines explicitly.
Manipulation. Deception. Short-term gains with catastrophic long-term consequences.
Black hat tactics destroy rankings permanently.
Black Hat SEO Tactics (Never Recommended)
Explicitly Forbidden Practices:
Keyword Stuffing: Excessive keyword repetition for manipulation. Destroys readability, triggers penalties.
Cloaking: Showing different content to users vs. search engines. Direct guideline violation.
Hidden Text: White text on white background, CSS hiding text. Obvious deception detected instantly.
Link Schemes: Buying links, PBN usage, excessive link exchanges. Manipulates PageRank, triggers Penguin penalties.
Scraped Content: Copying content from other sites without permission. Plagiarism plus SEO violation.
Automated Content: Mass-generated thin content without human review. Triggers Panda filter.
Doorway Pages: Low-quality pages targeting specific keywords redirecting to the main site. Pure spam.
Negative SEO: Building spammy links to competitors to harm their rankings, unethical and often ineffective.
Black Hat Consequences:
Algorithmic Penalties: Traffic drops 50-90%+ overnight.
Manual Actions: De-indexation requiring reconsideration requests, months to recover if approved.
Brand Damage: Reputation harm if tactics are exposed publicly.
Recovery Time: 6-18 months minimum to recover from severe penalties.
Business Risk: Complete loss of organic channel, existential threat.
Famous Black Hat Penalty Cases:
- JCPenney (2011): Link scheme penalty, lost 50%+ traffic
- Overstock (2011): Edu link scheme, temporary rankings loss
- Rap Genius (2013): Link scheme, de-indexed temporarily
- BMW Germany (2006): Cloaking, completely de-indexed
The Black Hat Gamble:
Some sites use black hat successfully short-term:
- Affiliate sites with low brand value
- Churn-and-burn domains
- “Test” sites for tactics
However, for any legitimate business with long-term goals, black hat is an existential risk.
Rankings appear. Rankings disappear. Business collapses.
At Cloudex Marketing, we NEVER use black hat tactics.
The risk is too high. The ethical issues are too severe. The sustainable results don’t justify manipulation.
Our reputation depends on client success, black hat jeopardizes that completely.
The Choice: Short-Term Gains vs. Long-Term Survival
White hat: Slow build, sustainable results, zero penalty risk.
Gray hat: Medium speed, moderate risk, uncertain future.
Black hat: Fast rankings, catastrophic penalties, business extinction.
The question isn’t “which tactics rank fastest?”
The question is: “Which approach keeps you ranking in 3 years?”
White hat wins every time.
Conclusion
After examining 30+ SEO types, the ultimate question remains:
- Which types should YOU prioritize?
Here We’ve Got the Solution For You:
Tier 1: Foundation (Required for All Sites)
- Technical SEO > Without crawlability, nothing else matters
- On-Page SEO > Topical clarity determines indexation quality
- Content Quality > User value drives sustainable rankings
Implementation Order:
Month 1-2: Technical audit + critical fixes
Month 2-3: On-page optimization + content audit
Month 3+: Ongoing content creation
Tier 2: Authority Building (Scales Impact)
- Link Building > Authority transfer accelerates rankings
- Off-Page SEO > External validation signals trust
Implementation Order:
Month 3+: Begin link building (after technical/on-page foundation)
Month 4+: Scale based on resources
Tier 3: Specialized (Based on Business Type)
If Local Business:
Local SEO (Google Business Profile, citations, reviews) would be the solution.
If E-commerce:
E-commerce SEO (product schema, category optimization) is for you.
If International:
Go with International SEO (hreflang, localization).
If Content-Heavy:
Semantic SEO (topical authority, clusters, and networks) is best for you.
If Large Enterprise:
You should go with Enterprise SEO (scale management, stakeholder alignment)
Tier 4: Emerging Opportunities (Future-Proofing)
- Voice/AI SEO > Preparing for AI Overview citations
- Video SEO > YouTube’s massive search volume
- Image SEO > Visual search growth
Implementation Timeline: After foundational types are solid (6+ months), experiment with emerging types, testing ROI.
The Action Plan (Next 90 Days):
This is a 90-day SEO roadmap that systematically guides you from audit to scaling. Its specialty: semantic SEO integration with entities, topical authority, and NLP optimization. Not just technical fixes.
It prioritizes high-impact tasks, prevents overwhelm, and follows a rigour framework for building holistic topical authority that search engines reward with sustained rankings.
Ready to transform your SEO strategy? Download the complete checklist and start crushing your rankings today!
The Ultimate SEO Type Selection Question:
Which SEO type has the highest ROI for MY business right now?
The Answer Depends On:
- Current State: What’s broken? (Fix technical first)
- Business Model: Local? E-commerce? B2B? (Determines specialized types)
- Resources: Budget? Team? Time? (Influences pace and scope)
- Competition: What are competitors doing? (Identify gaps to exploit)
- Goals: Traffic? Conversions? Brand? (Aligns tactics to outcomes)
No universal answer exists, but the framework above enables informed decisions.
Final Thoughts
Google’s documentation confirms the future of search prioritizes understanding meaning over matching strings.
The old approach targeted keywords to rank for exact phrases and capture that search volume. The new approach optimizes topics comprehensively to rank for related queries and capture broader search intent.
The 30+ SEO types covered in this guide are tools, means to the end of topic recognition and topical authority.
Choose types strategically based on your business focus, implement them systematically following Google’s ranking systems, and measure rigorously using comprehensive metrics beyond just keyword rankings.
Ready to implement SEO under an expert’s guidance?
Cloudex Marketing’s SEO audit service provides a comprehensive analysis across all SEO types, identifying which strategies deliver maximum ROI for YOUR specific business niche, competitive landscape, and resource constraints.
Our technical SEO services establish the foundational infrastructure enabling all other SEO types to function properly, crawlability, indexation, Core Web Vitals optimization aligned with Google’s documented ranking systems.
Local SEO services dominate geographic search through Google Business Profile optimization, citation building, and review management strategies proven across 40+ local campaigns.
The SEO universe is vast, but with the right framework, measurable progress is achievable in 90 days.
Start with Technical and On-Page SEO. Build authority through Link Building and Off-Page tactics. Specialize based on business type. Future-proof with emerging SEO types.